Affiliate links on Android Authority may earn us a commission. Learn more.
Photography terms explained: ISO, aperture, shutter speed, and more

Photography is much more than pointing a camera and pressing a button. This is something you realize soon after getting your hands on a serious shooter. Maybe you stumbled upon your smartphone’s manual mode and asked yourself what all these settings are. There’s a lot to learn in this endless pit of photography terms, settings, skills, and techniques.
Becoming proficient in photography will take more than reading this post, but you can use this as a general guide to get started. Here you will find the most important terms and concepts revolving around the art of photography. You can also bookmark this page and come back to it to refresh your knowledge or clear any future doubts.
Photography is much more than pointing a camera and pressing a button.Edgar Cervantes
Photography terms
The exposure triangle in photography
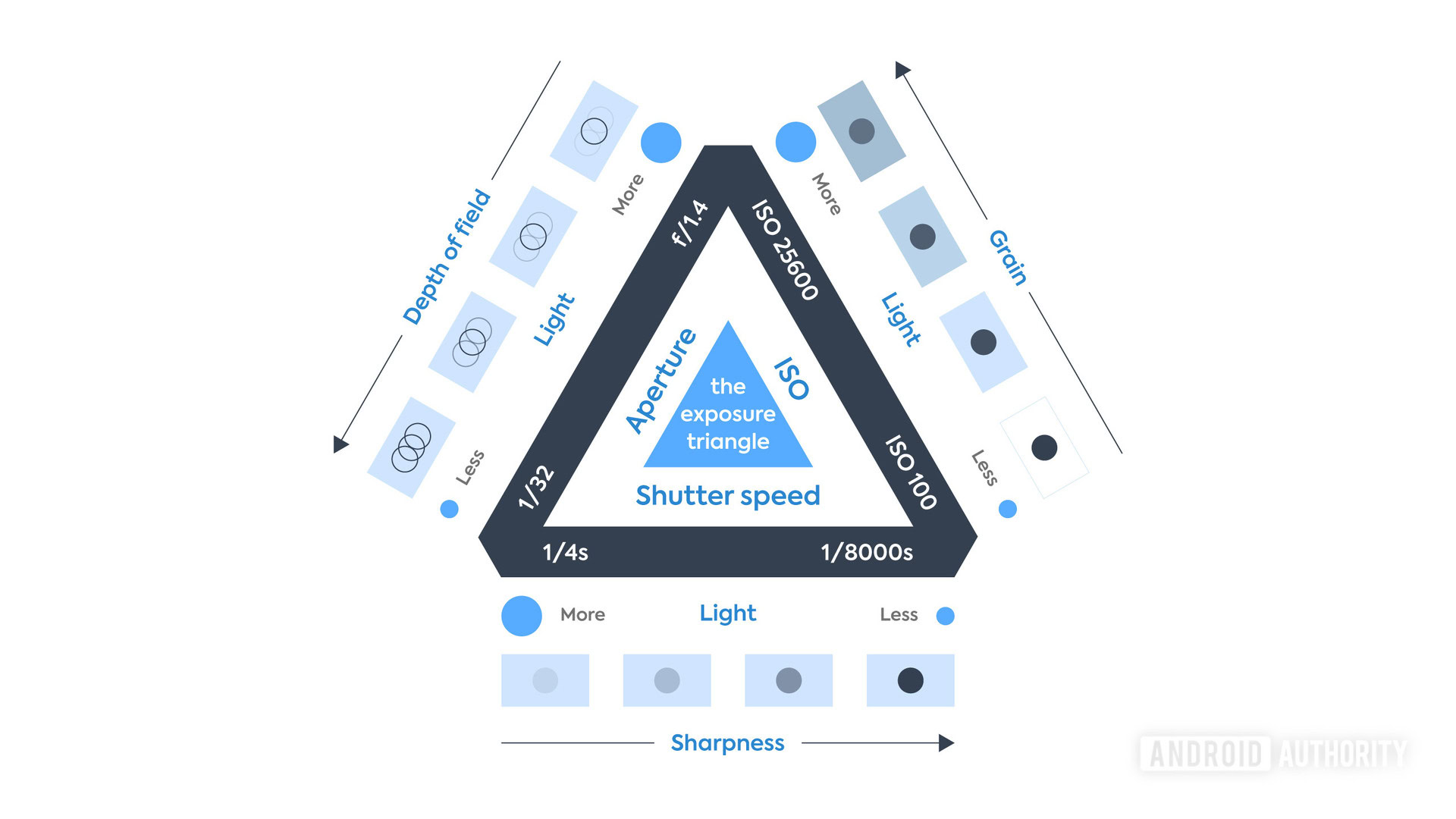
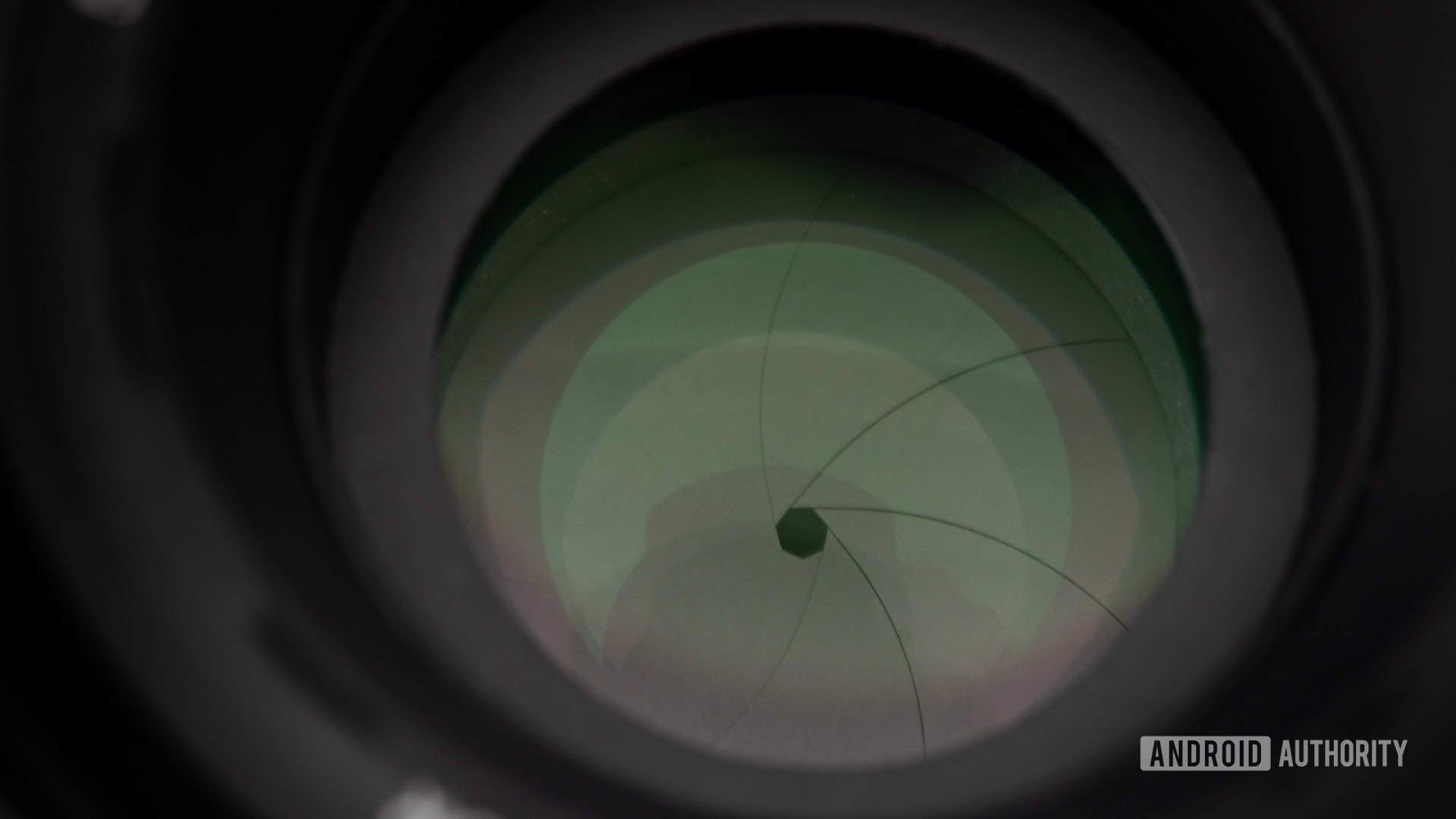
This is the first thing you need to learn if you want to dive into the world of serious photography. The exposure triangle consists of three settings you need to keep in check to expose an image properly. These are aperture, shutter speed, and ISO. Let’s touch a bit on each one of them.
The exposure triangle is the first thing you need to learn when getting serious with photography.Edgar Cervantes
Aperture
This is a photography term you’ve probably heard often. Aperture is defined by the size of the opening through which light can enter the camera. It is measured in f-stops, a ratio of the focal length divided by the opening size. The smaller the f-stop, the wider the opening. An f/1.8 aperture is wider than f/2.8, for example.
Aperture has one main effect in photographs, which is depth of field. Using a wider aperture like f/1.8 will create a smaller depth of field. This will enhance bokeh, the popular blurry background effect in photos. Tightening the aperture will keep more in focus.
Shutter speed
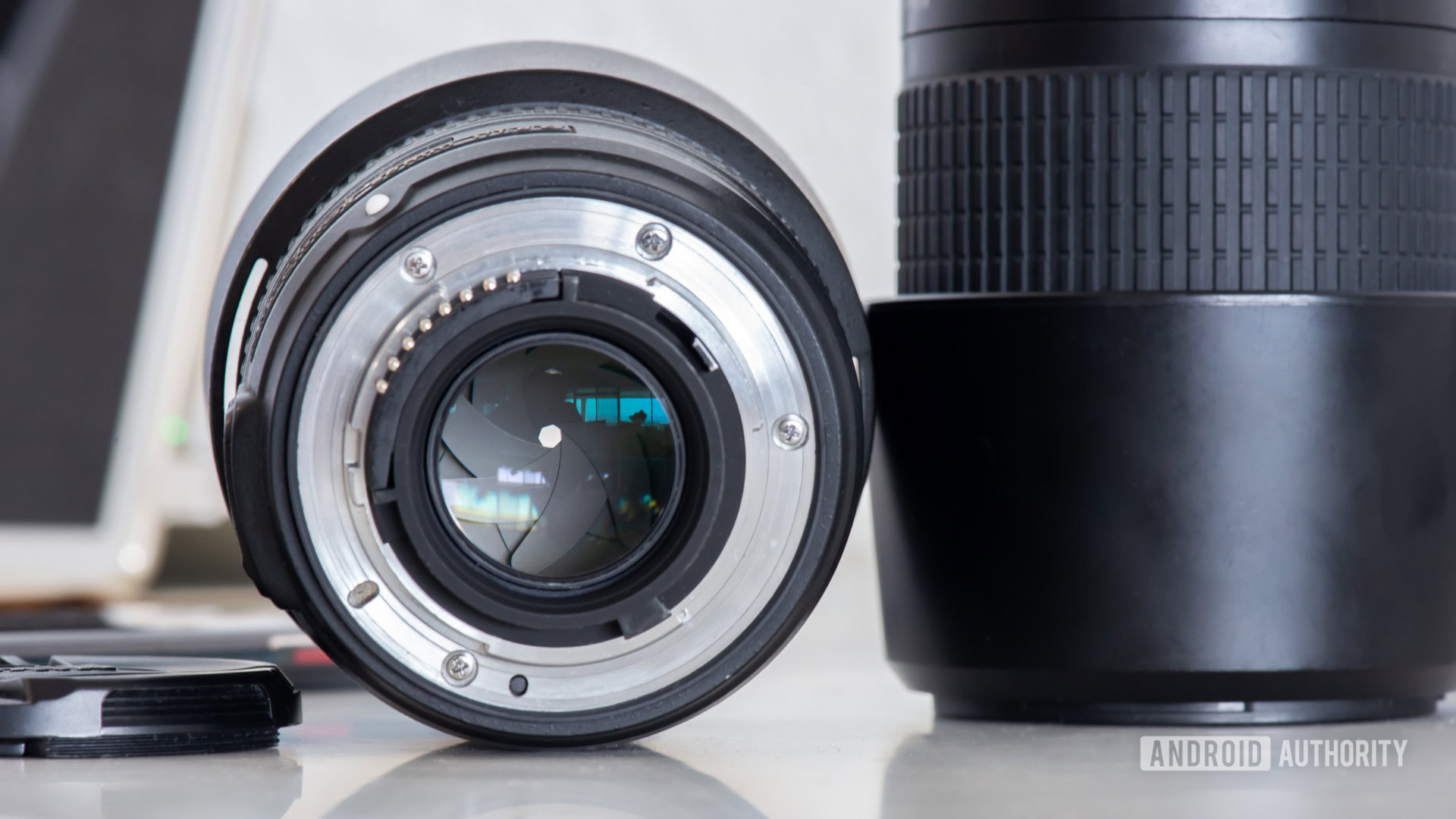

A camera needs to let light into the sensor to take a photograph. Cameras have a shutter, which stops light from reaching the sensor until activated. The shutter will open up and expose the sensor to entering light when you press the shooting button. Shutter speed refers to the time the shutter stays open.
Motion blur is not always a bad thing!Edgar Cervantes
Shutter speed is typically measured in seconds and fractions of a second. A shutter speed of 1/100 will expose the sensor for a hundredth of a second. Likewise, a 1/2 shutter speed will last half a second. You can also leave the shutter open for multiple seconds, commonly referred to as a long exposure shot.
A faster shutter speed better freezes the scene. Elongating shutter speed will brighten an image, but it can also create motion blur (which is not always bad).
ISO

The following photography term on our list is ISO, which relates to sensor (or film) sensitivity to light. A lower ISO makes the sensor less sensitive to light, meaning it needs more illumination or a longer shutter speed to expose an image properly. Increasing the ISO makes your sensor more sensitive to light, allowing you to shoot in darker environments, with tighter apertures, and/or using faster shutter speeds.
Increasing the ISO creates more grain or noise. Edgar Cervantes
Photographers measure ISO in numbers. While manufacturers used to stick to ISO 100, 200, 400, 800, 1600, and so on (doubling in value), things have changed with more recent cameras. Smaller increments have been introduced for better refinement, but the concept is the same. ISO 100 is half as sensitive as ISO 200, which is also half as sensitive as ISO 400.
The effects of ISO are simple to understand. A higher ISO will make a sensor more sensitive, making an image brighter. At the same time, increasing the ISO creates more grain or noise.
What are the M, S, A, and P camera modes?

The M, A, S, and P modes in most DSLR and mirrorless cameras offer different shooting styles, from full manual to assisted exposure compensation.
- M: Manual
- A: Aperture priority
- S: Shutter priority
- P: Program mode
To learn more about what each shooting mode does and how to use it efficiently, check our guide below.
Aperture priority
Most cameras featuring this shooting mode label it as “A,” and one would usually find it in more advanced bodies like DSLRs, mirrorless, and mid-to-high-end point-and-shoot cameras.
The mode’s name explains precisely what aperture priority does: prioritizing aperture as the only setting you have to worry about. Aperture priority is much like auto mode, but grants control over aperture and automates only shutter speed. Once your ISO is set, the camera will allow you to open or close the aperture using a dial. The appropriate shutter speed will be determined by the camera’s light meter and set for you automatically.
Macro
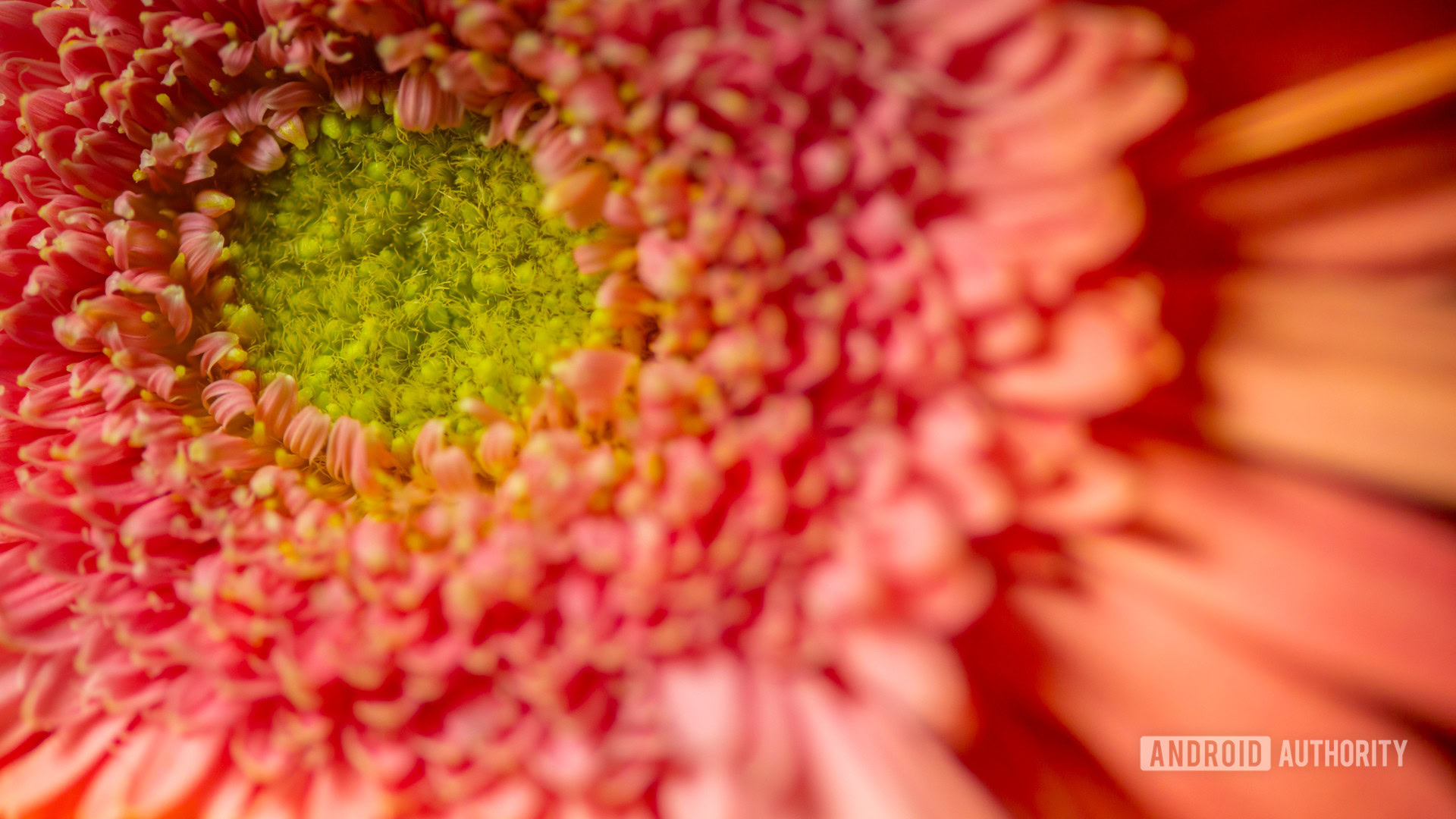

Macro photography refers to close-up, magnified images of tiny things. Typical examples are images of bugs, in which you can see them in so much detail you can even tell the minuscule hairs, eyes, and other details commonly unnoticeable to the naked eye. Other popular subjects are flowers, eyes, water droplets, and many other tiny objects.
Bokeh
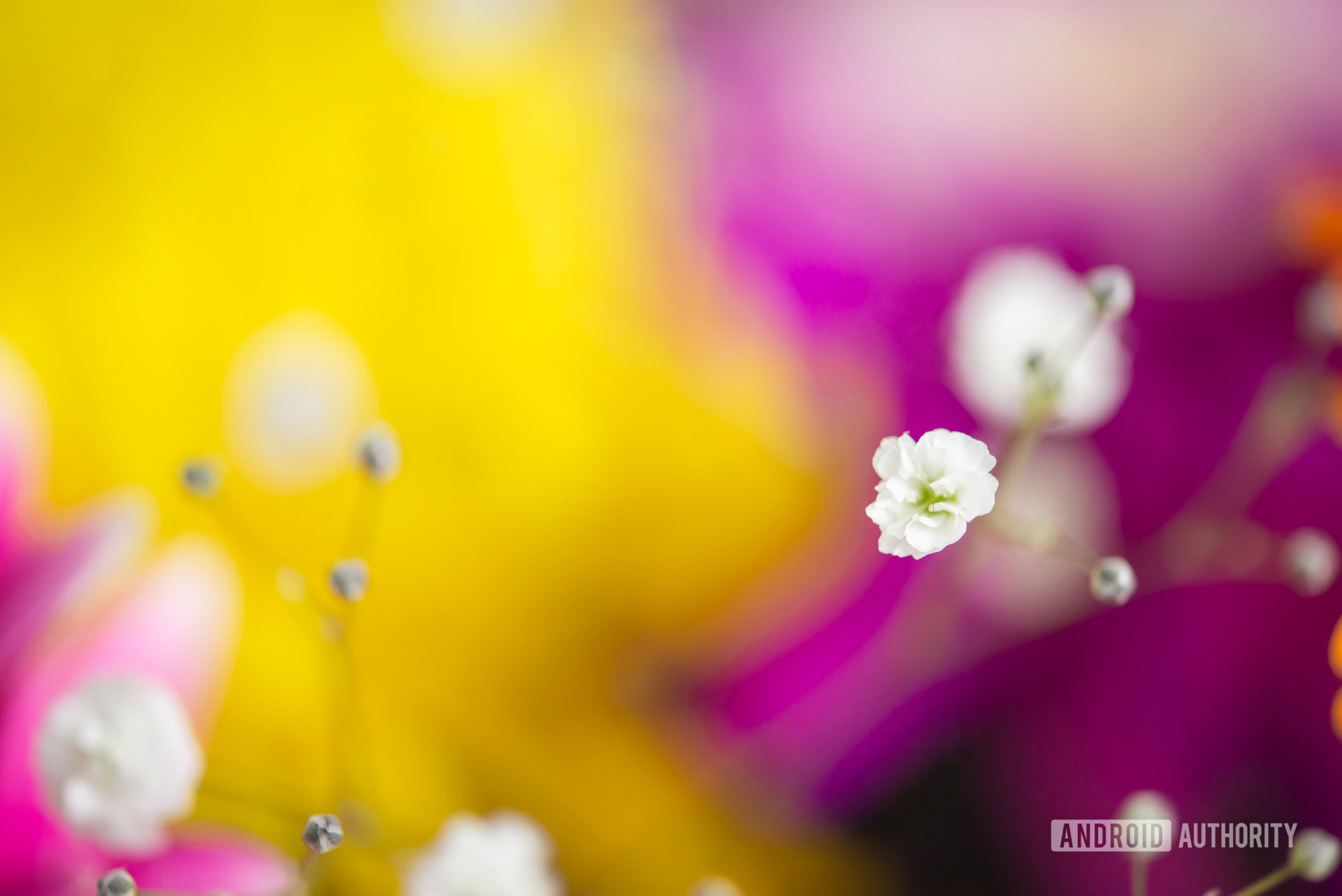

In simple terms, bokeh refers to the quality of the out-of-focus areas in a photograph’s background and foreground. Many believe it to be synonymous with background blur, which isn’t exactly true. Bokeh instead refers to how good that background blur looks.
Exposure compensation

If you have ever seen a camera button with “+” and “-” signs in it, that would be the exposure compensation controls, otherwise known as exposure value (EV). This will help when shooting in auto or semi-auto modes (aperture priority, shutter priority, etc.).
Cameras try to get the correct exposure by measuring light, but they don’t always get what you intended to capture. You may not even want a well-exposed image. Sometimes, you want things to look a little darker to add mood. With exposure compensation, you can tell the camera it’s capturing exposure incorrectly, and it will make up for it by adjusting other settings (usually ISO).
We measure exposure compensation by f stops like so: –1.0, –0.7, –0.3, 0.0, +0.3, +0.7, +1.0. In this case, -1.0 would be one stop less, while +1.0 is a stop higher.
Dynamic range in photography

The Oxford Dictionary defines the photography term ‘dynamic range’ as “the ratio of the largest to the smallest intensity of sound that can be reliably transmitted or reproduced by a particular sound system.” That definition refers to audio, but the idea is similar in photography. This term relates to how much data a camera can capture at the extremes of exposure in a scene, from the darkest to the lightest parts of a scene.
You measure dynamic range in stops, where each stop equals double or half the amount of light. Increasing exposure by one stop means doubling the light. If you were shooting at shutter speed 1/100, one stop brighter would be 1/50, while one stop darker would be 1/200.
Focal length
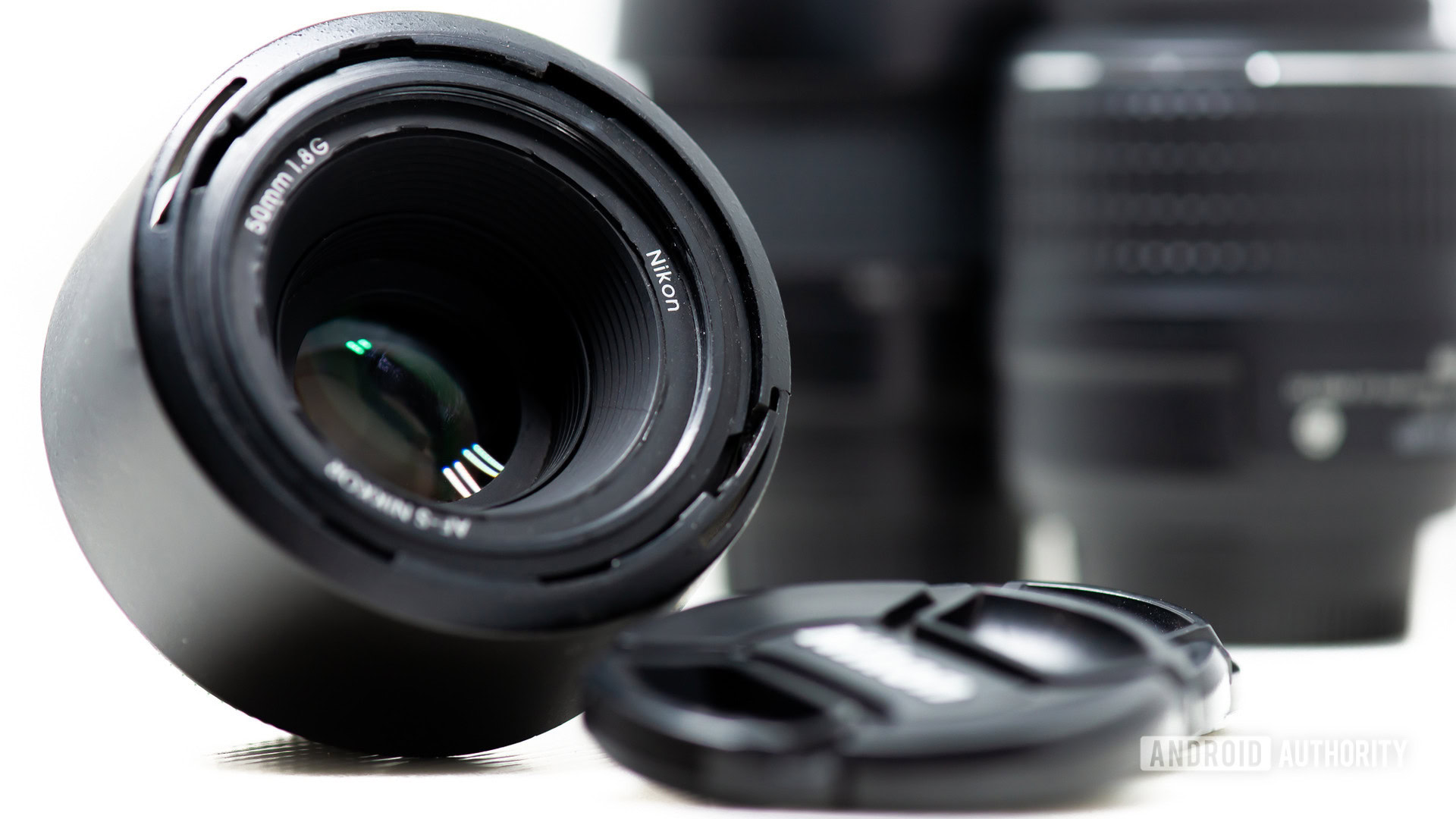

Put simply, focal length is the distance between a camera sensor (or film) and a lens’s point of convergence.
The hardest part is understanding what the point of convergence is (also known as optical center). When light rays enter a lens, they travel through glass and bend to converge in a single point. This point is where light data is collected to form a sharp image for the sensor to record. Manufacturers measure the focal length focused to infinity to keep a standard.
Focal length is measured in millimeters. A 50mm lens will have a 50mm (or 5cm) point of convergence from the sensor. Focal length also determines how “zoomed in” you are, changes perspective, and affects depth of field.
Photography zoom types: Optical, digital, and hybrid

In photography, camera zoom refers to making a subject appear closer or farther away in an image. Zooming in gives you a closer look at objects, while zooming out will let you capture a wider space. Cameras use three types of zoom technology: optical, digital, and hybrid.
Optical zoom is achieved using a series of lens elements. Glass can move through the lens to zoom in or out. Digital zoom achieves a similar effect without mechanical work or glass elements. It will essentially cut off areas around your scene to make it seem like you are closer to the subject. Digital zoom is technically cropping. Hybrid zoom is a whole new photography term/concept. It uses optical zoom, digital zoom, and software to improve results when zooming in further than the lens’s physical capabilities.
White balance

The following photography term we’ll discuss is White balance, which refers to the effects color temperature and tint have in photographs. Different light sources emit varying color temperatures, ranging in a spectrum between orange and blue. Likewise, light comes with tint, which ranges between green and magenta. Changing the white balance settings will help you balance these colors and achieve a more natural effect.
Color temperature is measured in kelvins (K). In photography, we have certain white balance options to help figure out the correct kelvin levels one should use under different circumstances.
- Candlelight: 1,000-2,000K
- Tungsten bulb: 2,500-3,500K
- Sunrise/sunset: 3,000-4,000K
- Fluorescent light: 4,000-5,000K
- Flash/direct sunlight: 5,000-6,500K
- Cloudy sky: 6,500-8,000K
- Heavy clouds: 9,000-10,000K
Megapixels (MP)
A megapixel simply means a million pixels. This photography term serves as a method of measuring definition in any image sensor. If a camera were to have a 12MP sensor, it means the images it takes are formed by twelve million pixels. This would be equal to a 4,000 x 3,000 resolution.
RAW vs. JPEG
A RAW image is known as an uncompressed, unedited image file. It keeps all data captured by the sensor, making it a much larger file with no quality loss and more editing power. This is why RAW data by itself isn’t much to look at.
RAW should only be used if you’re planning on going back to edit your pictures.Edgar Cervantes
RAW should only be used if you plan to go back to edit your pictures. The file sizes are much larger, but this allows you to tweak your pictures’ full exposure and color settings, bypassing the camera’s default image processing.
While saving a picture to JPEG chucks away image data and compresses the picture, this is perfectly fine if you’re planning to upload a photo to Facebook or take a quick snap for your gallery.
Image stabilization
OIS
OIS compensates for small movements of the camera during exposure. In general terms, it uses a floating lens, gyroscopes, and small motors. The elements are controlled by a microcontroller that moves the lens very slightly to counteract the camera’s shaking — if the camera moves to the right, the lens moves left.
This is the best option because all stabilization is done mechanically, not through software, which means no quality is lost in the process.
EIS
Electronic image stabilization works through software. Essentially, EIS breaks up the video into chunks and compares it to the previous frames. It then determines if movement in the frame was natural or unwanted shake, and corrects it.
EIS usually degrades quality, as it needs space from the content’s edges to apply corrections. It’s improved in the last few years, though. Smartphone EIS usually takes advantage of the gyroscope and accelerometer, making it more precise and reducing quality loss.
Autofocus photography terms
Smartphone cameras generally use five types of autofocus systems: dual-pixel, quad-pixel, all-pixel, phase-detect, and contrast-detect. We will tell you about them in order, from worst to best.
Contrast-detect autofocus
This is the oldest of the three and works by measuring contrast between areas. The idea is a focused area will have higher contrast, as edges will be sharper. When an area reaches a particular contrast, the camera will consider it in focus.
Phase-detect autofocus
“Phase” means that light rays originating from a specific point hit opposing sides of a lens with equal intensity. In other words, they are “in phase.” Phase-detect autofocus uses photodiodes across the sensor to measure phase differences. It then moves the focusing element in the lens to bring the image into focus.
Dual-pixel autofocus
This is easily among the best autofocus technologies available. Dual-pixel autofocus is like phase-detect, but it uses more focus points across the sensor. Instead of focusing on dedicated pixels, each pixel comprises two photodiodes that can compare subtle phase differences to calculate where to move the lens.
Quad-pixel autofocus
A Quad Pixel setup splits a pixel into four. Each pixel in a Quad Pixel PDAF system can analyze left/right and top/bottom. This alleviates the issue with horizontal autofocus and is even more reliable and accurate than Dual Pixel PDAF.
All-pixel autofocus
All Pixel Omni-Directional PDAF is OPPO’s nomenclature for the autofocus afforded by Sony’s 2×2 OCL sensor. 2×2 OCL is essentially a Quad Pixel Quad Bayer set up with one condenser lens per pixel, covering all four photodiodes. 100% of an image sensor’s pixels are used for both focusing and imaging.
HDR photography
HDR accomplishes a balanced exposure throughout the frame. You do this by shooting multiple images at different shutter speeds. The idea is that each photo will expose for different light levels. The image conglomerate is merged, becoming a single photo with much more information in both the bright and dark sections.
Pixel binning
Pixel-binning is a process that sees data from four pixels combined into one. So a camera sensor with tiny 0.9-micron pixels will produce results equivalent to 1.8-micron pixels when taking a pixel-binned shot. This technique is mainly used in smartphones, which are forced to use smaller sensors due to size restrictions.
The biggest downside of this technique is that your resolution is effectively divided by four when taking a pixel-binned shot. So that means a binned shot on a 48MP camera is actually 12MP, while a binned shot on a 16MP camera is only four megapixels.
Portrait mode in smartphone photography

Portrait mode is used to describe the artificial bokeh (BOH-kay) effect produced by smartphones. Bokeh is a photography effect where the subject of a picture is kept in focus while the background falls out of focus. Using portrait mode to create a bokeh effect, you can take dynamic photographs that look more professional.
Night Mode in smartphone photography

Night Mode (Dark Night, Nightscape, or whatever your manufacturer may call it) uses artificial intelligence to analyze the scene you are trying to photograph. Your phone will take into account multiple factors, such as light, the phone’s movement, and the movement of objects being captured. The device will then shoot a series of images at different exposure levels, use bracketing to put them together, and bring out as much detail as possible into a single picture.
Of course, there is a lot more going on behind the scenes. The phone must also measure white balance, colors, and other elements, usually done with fancy algorithms most of us don’t fully understand.
Super Resolution
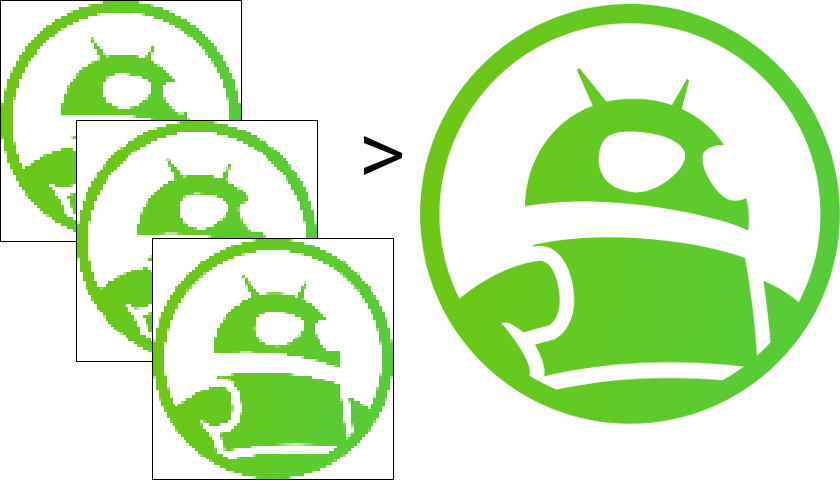
Super-resolution is the practice of generating a higher resolution image by taking and processing multiple lower resolution shots. By taking various lower resolution shots and comparing these points in each image, you’ve got the foundation for a solid, higher resolution image. What’s essentially happening is that there are minor differences between these points, and algorithms or machine learning techniques can use these differences to fill in the gaps and create additional detail.
Computational Photography
Size matters in photography. Because smartphone sensors and lenses aren’t getting much bigger, smartphone manufacturers need to figure out ways to get more out of less. Enter the age of Computational Photography.
This photography term can get pretty complex, but it simply refers to image improvements with the help of software and complex algorithms. Some examples of Computational Photography are AI enhancements, night mode, pixel binning, portrait mode, HDR, and others.
Deepfake photography and video

We’ll talk about an exciting photography term in this post: Deepfake, an AI (artificial intelligence) technique that uses machine learning to create or manipulate content. It is often used to create montages or superimpose a person’s face on top of another, but its capabilities extend far beyond that. This technology has plenty of other applications. These include manipulating or creating sound, movement, landscapes, animals, and more.
DSLR camera

DSLR stands for “digital single-lens reflex.” This type of camera has been among the most popular until the arrival of mirrorless cameras. These are the big cameras you see serious photographers carrying around when they mean business.
DSLR cameras use reflections to bring the image up to the viewfinder using either a pentaprism or a series of mirrors. The mirror flips up and lets light reach the sensor when a photo is triggered. And while it’s not part of the definition, the norm is that DSLR cameras have an interchangeable lens system.
The main benefit of DSLRs is that you view an exact reflection when looking through the viewfinder. It’s not a digital image or a reproduction of what’s actually happening. What you see is in real-time and literally travels at the speed of light.
Mirrorless camera

A new era is upon photographers, and it seems mirrorless cameras are phasing out DSLR cameras. As their name implies, these have no mirrors or reflective prisms. Instead, the sensor captures all light information, and the camera processes it directly. Whether you use a viewfinder or a screen, you will get a digital reproduction of what the sensor is seeing.
This allows the camera’s computing power to help, giving cameras more capabilities like seeing your results before shooting an image. In addition, autofocus is faster, cameras can shoot at more frames per second, and bodies are much smaller.
Tripod
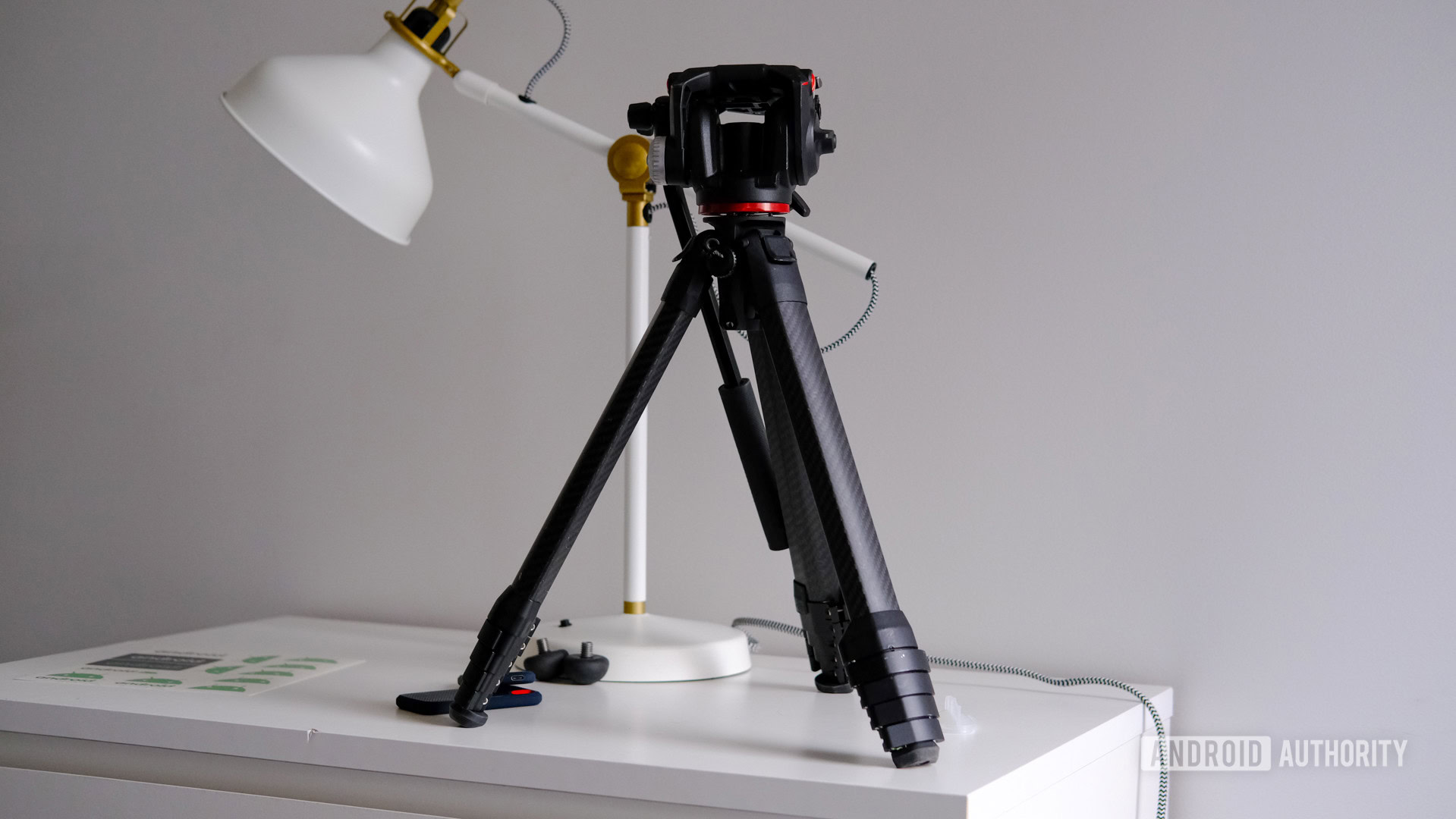

Tripods are stands with three collapsible legs designed to hold your camera static. They are braced around a center post for maximum stability and feature a smartphone or camera mount on top, as well as several joints that allow you to rotate and tilt your device.
These accessories bring stability to your camera, allowing you to get crisper images at low shutter speeds, create long-exposure shots, set a timer, get yourself in a picture, and more. Tripods are essential, so definitely learn more about this photography term.
Monopod
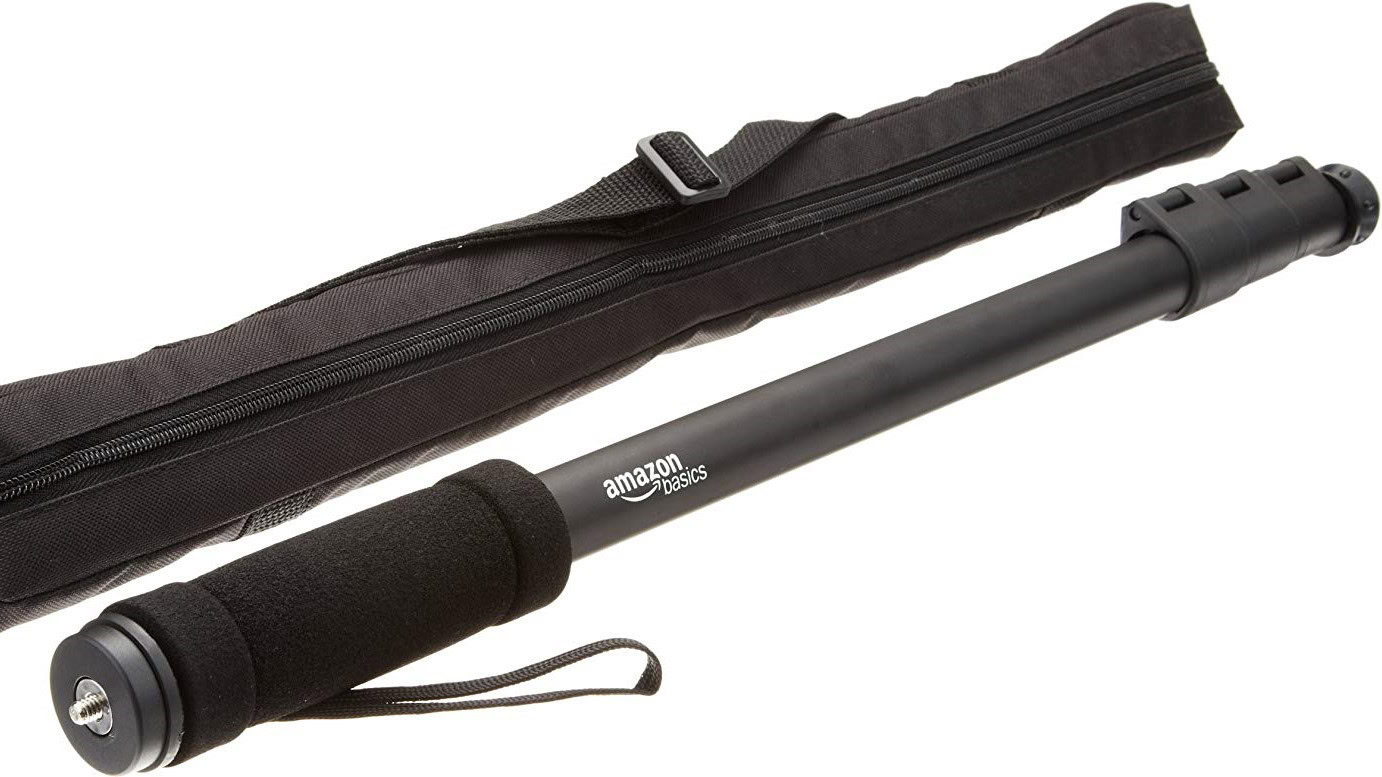

Monopods serve a similar purpose to tripods, but they do so in a smaller, lighter form factor that is much more portable and convenient. These are not as stable as tripods, but they still help stabilize a camera while staying light.
Selfie stick
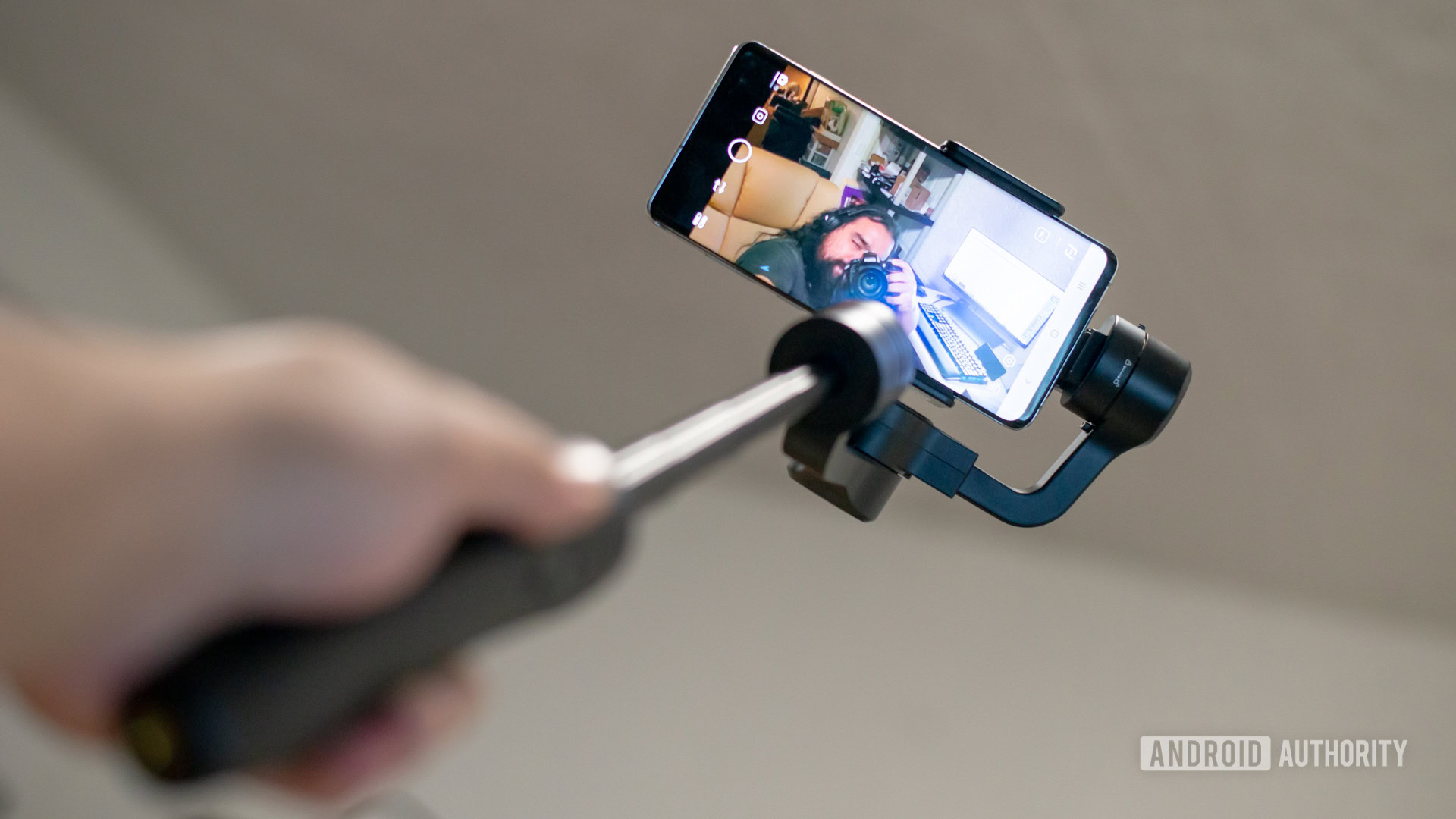

Taking a selfie looks and feels uncomfortable, especially if your selfie shooter doesn’t have a wide-angle lens and you need to get more people in the frame. That’s where selfie sticks come into play!
Here’s another photography term for you. A selfie stick is an artifact in which you can dock a smartphone. These work as an extension of your arm and can be extended so that your phone is further away from the subject.
You can connect these via Bluetooth and have buttons in the handle, so that you may take photos from a distance. Some older ones may connect to your phone through a 3.5mm headset jack, but most modern phones lack that port.
Gimbal or stabilizer
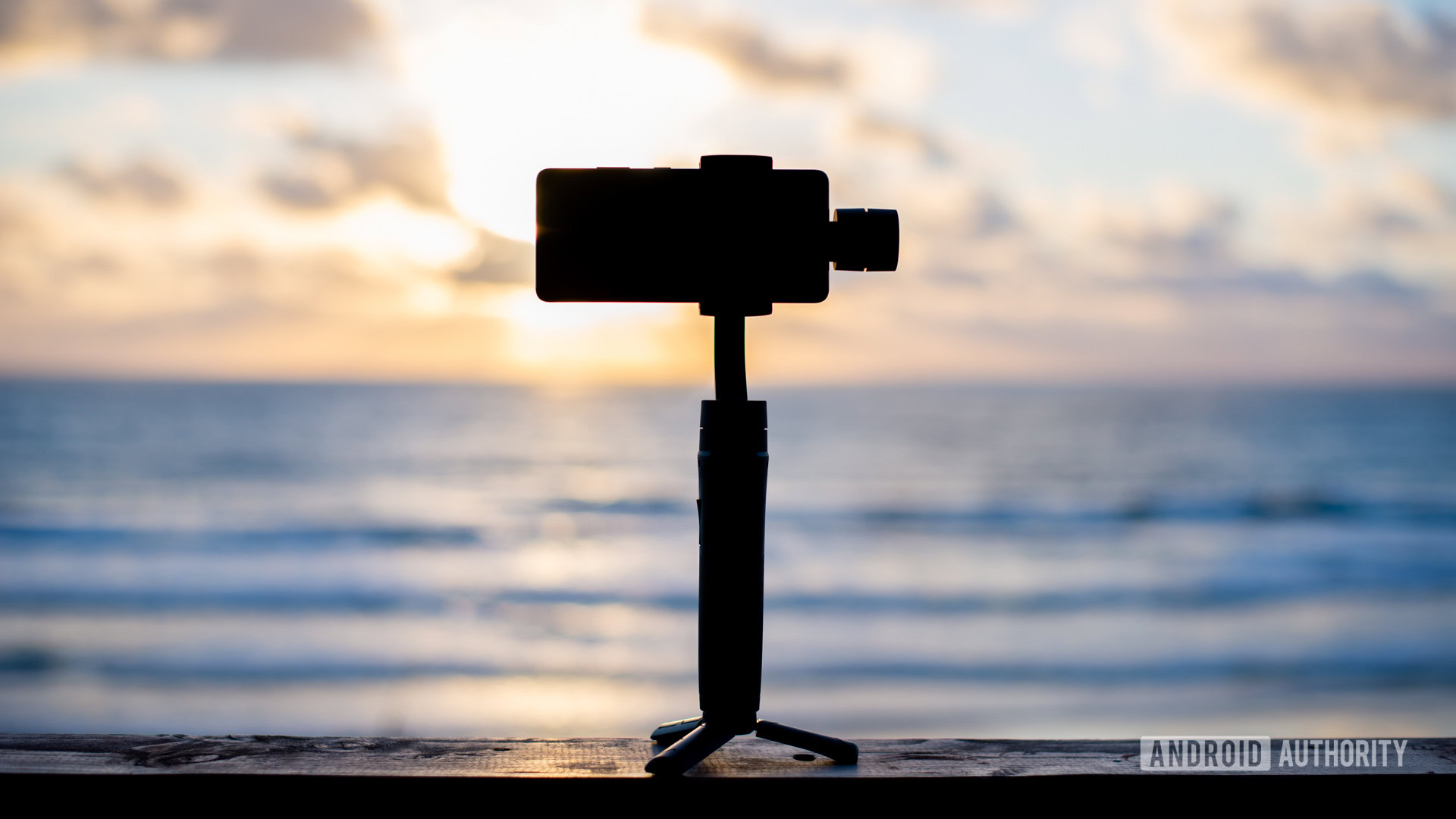

You’ve probably seen some serious videographers carrying around contraptions to keep their cameras steady. These are gimbals or stabilizers. They use a series of motors and sensors to keep a camera or smartphone from moving around too much, therefore creating smoother video footage or less blurry images.
There are different types of gimbals. Do you want a 3-axis or 2-axis gimbal? 2-axis stabilizers smooth out tilt and roll, which means movements going up/down or from side to side. The third axis steadies panning, but requires a more complex mechanism and a larger, more expensive body.
Hit the button below to learn more about gimbals and which you should consider buying.
Bonus: Check out more photography posts!
Have you had enough yet? Well, we have more photography content for you! Take a look at some of our featured posts and tutorials to keep improving your skills.
- What a pro photographer can do with a cheap Android phone camera — Android Authority dared me to take some awesome pro-level photos using a $130 phone. Here are my results.
- Photography tips: Rule of thirds, viewpoint, framing, color theory, and more — Are you past photography basics? Here are some more advanced concepts to study.
- Smartphone photography tips: 16 handy tricks you should know — Don’t feel limited if your primary camera is a smartphone. You can take fantastic imagery too.
- The best Android camera phones — Maybe all you need is a good camera phone. Here is a list of the best ones.
- Budget camera phones worth the money — Often, the best Android camera phones can get very expensive. This list is for those who want the best possible smartphone camera on a budget.
- Ten best photography apps for Android — You will need to throw some apps into that phone.
- Tips for editing on Lightroom — Those looking to edit their photos can use these tips to improve images without doing crazy edits.
- The best digital photo frames — Show off your creation with a physical, yet modern photo frame.
- What to expect from smartphone cameras in 2022 — See what’s new in the smartphone industry.