Affiliate links on Android Authority may earn us a commission. Learn more.
What is generative AI and how does it work?
If you’ve read about the buzz surrounding chatbots like ChatGPT and image generators like Midjourney, you may have come across the term generative AI. The term is usually used to describe modern artificial intelligence systems that can mimic humans and perform complex tasks within seconds. Generative AI is particularly impressive in creative tasks like drawing and writing poetry, which computers have historically struggled with. But what has spurred the sudden explosion in generative AI and how does the technology work? Here’s everything you need to know.
What is generative AI?
Generative AI is a catch-all term used to describe computer programs that can generate text, images, videos, and audio all on their own. Some examples of generative AI include ChatGPT, Midjourney, Github Co-pilot, and Google’s Duet AI for Workspace.
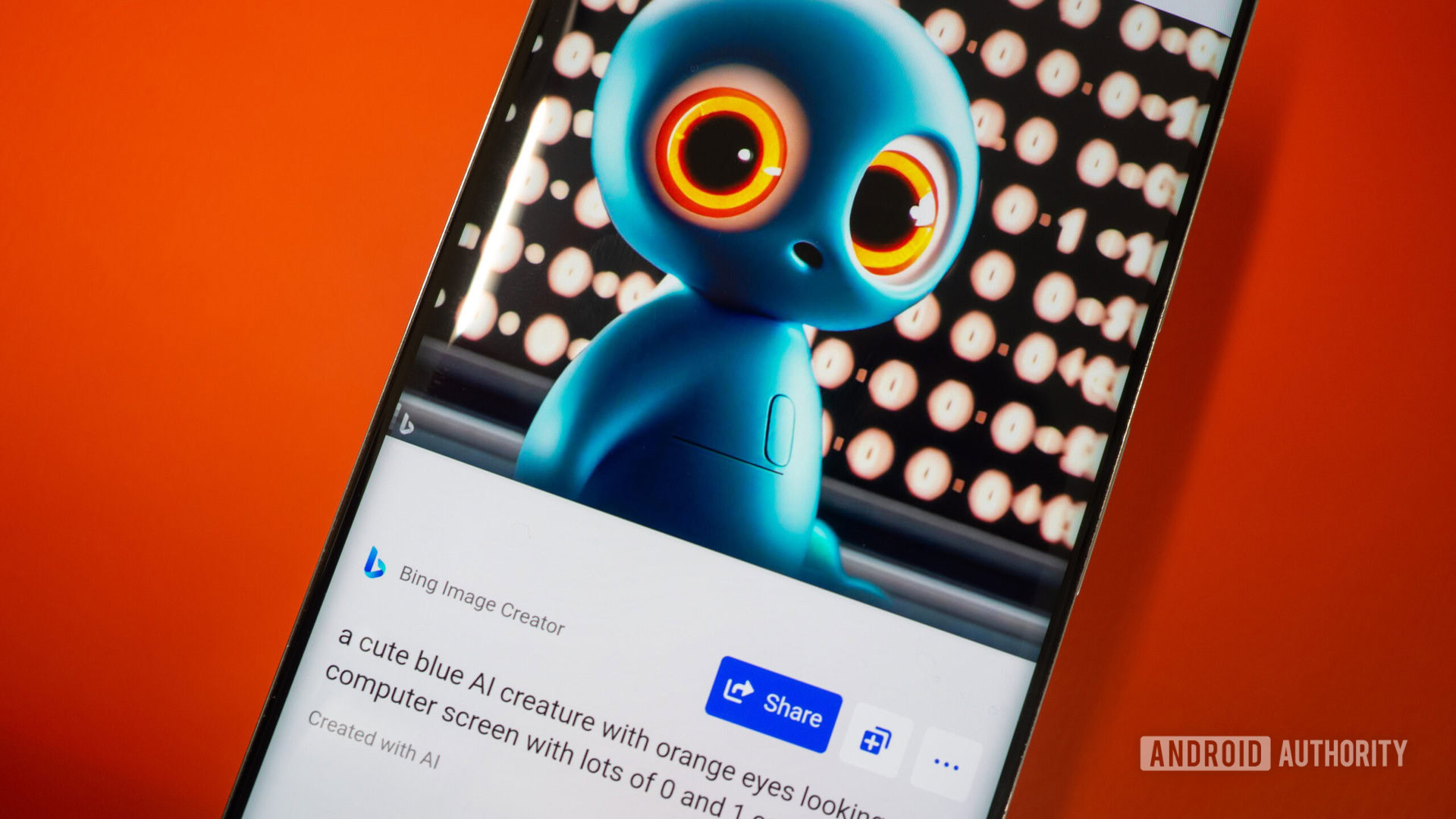
Up until this point, most AI systems weren’t very creative and would deliver far worse results than a human. However, that’s no longer the case with generative AI. For example, you can ask a generative AI tool like Bing Image Creator to create a photorealistic image of a “cute blue AI creature with orange eyes” and it will deliver the results you see above. The tool in question wasn’t explicitly taught or trained to produce this image, but it delivered an impressive result anyway.
Generative AI can create text and art in an instant.
Generative AI tools have become increasingly capable, with new developments landing every few months. The latest version of an AI image generator even managed to fool experts and win a prestigious photography competition. Likewise, several AI-generated images have gone viral on social media, including some with a political agenda.
So whether or not you’re planning to use generative AI for yourself, it’s important to know that they exist and what their limitations are. Thankfully, we have not reached the point where these tools are perfect. In fact, they’re prone to making some glaring mistakes. This means that you can distinguish between real and AI-generated content with the right information and training.
How does generative AI work?
Generative AI falls under the category of machine learning, which is a broad term used to describe any computer algorithm that analyzes large amounts of data. These algorithms are designed to mimic the way humans perform tasks.
The first step is to extract patterns from existing data, so if you want an AI that can generate new faces, you’d feed in a dataset containing images of faces. With enough training, the algorithm will learn what a face looks like as well as common features like a nose, eyes ears, and lips. From there, it can start working on smaller details like expressions, facial hair, and skin tones.
Generative AI can make glaring mistakes, but you'll need to look closely.
Without enough training, the machine learning model in our example won’t produce results that look like a human face. In fact, this very problem is currently affecting AI image generators like Midjourney. Experts were able to quickly detect fictional images of Pope Francis through careful examination of the fingers visible in the image. Since photos of people holding objects don’t include full fingers, generative AI algorithms can struggle to gather enough information from the training data.
Transformers and reinforcement learning
Many of the modern generative AI tools you may have heard about, including ChatGPT, rely on the Transformer architecture. Transformers allow the algorithm to focus on relationships within the data. So in a large language model like GPT-3, for example, they make predictions about which word is likely to appear next.
Reinforcement learning is another common technique used in generative AI. Put simply, a human manually scores the output of a model to filter out bad responses and nudge the algorithm to respond in a certain way. Thanks to a public research paper on the LaMDA language model, we know that Google hired part-time workers for reinforcement learning. Over time, their feedback helped the model deliver high-quality and useful responses to user prompts.
What are the benefits and limitations of Generative AI?

As with any new technology, we’re bound to see it used in creative and malicious ways simultaneously. Let’s start with the benefits of generative AI:
- Reduced manual labor: In tasks that involve a lot of repetition, generative AI can ease the burden with little to no effort. For example, computer code includes a lot of boilerplate text. A developer can automate most of the initial steps with the help of a chatbot.
- Increased efficiency: Computers can process large amounts of information significantly faster than any human. A language model can quickly summarize a long document or research paper and answer questions that require critical thinking. You can now even use AI to help you write a novel.
- Human-like decision-making: Generative AI can deal with new and unseen scenarios extremely well, meaning it could also excel at decision-making. GPT-4, for example, can already pass standardized tests designed for college students and solve complex math problems.
But as promising as cutting-edge AI tools are, there are plenty of downsides to them too. We already have a dedicated post addressing the dangers of AI, but here’s a quick summary:
- Bias: As mentioned earlier, generative AI tools only perform well after going through enough training. Unfortunately, however, endless variations in the real world make an unbiased or perfect AI quite out of reach today. An AI designed to select job applicants, for example, could unintentionally pick based on certain races or genders due to training biases.
- Malicious acts: From amateur programmers using ChatGPT to generate malware to social media users creating deepfake imagery of politicians, generative AI tools can already harm or mislead the general population with very little effort.
- Job loss: Generative AI has the potential to render some jobs obsolete or, at the very least, reduce hiring demand. This is particularly true in the art industry, where a single text-based prompt can produce images nearly instantly. A trained human can then spend only a short amount of time refining the AI-generated art rather than creating it from scratch.
What are some examples of Generative AI?
We’ve already discussed a few examples of generative AI throughout this article. But we can also go one step further and group them on the basis of their role.
- Text and dialog: Chatbots like ChatGPT, Bing Chat, and Google Bard fall under this category. They’ve been trained and fine-tuned to engage in back-and-forth conversation, making them perfect for tasks like research and customer support.
- Image and video: AI image generators like Midjourney, DALL-E 2, and Stable Diffusion can convert a few words into art. They can also work with existing images to replace backgrounds, add or blend in elements, and create upscaled copies of low-quality inputs.
- Speech and audio: Companies like Google have been working on using generative AI to synthesize speech. You might already be familiar with the WaveNet text-to-speech model since it’s used for the Google Assistant. But that’s not all, other generative AI like Google MusicLM can also create music with instruments and vocals in specific genres and styles.
- Code: What if computers could write their own programs? We’re not quite there yet, but programmers can already use an AI companion like GitHub Copilot or OpenAI Codex to speed up their workflows.
It’s worth noting that most of these generative AI tools didn’t even exist a few years ago. But with breakthroughs landing seemingly every other week, it’s impossible to predict what the future will bring.
FAQs
ChatGPT, Google Bard, and Midjourney are some of the most famous examples of generative AI.
AI is a broad term that refers to any system that exhibits human-like decision-making ability. Generative AI, on the other hand, specifically describes a system that can create unique human-like text, images, audio, or even videos.
