Affiliate links on Android Authority may earn us a commission. Learn more.
What is Conversational AI and how does it work?

When digital assistants like Siri and the Google Assistant first debuted in the 2010s, their ability to understand natural language was heralded as nothing short of revolutionary. Nearly a decade later, however, their sheen has worn off and conversational AI platforms like ChatGPT have taken stage instead. They can understand general language, including slang, without requiring you to parrot rigid commands each time. But what exactly does conversational AI mean and how does the underlying technology work? Let’s break it down.
What is conversational AI?
Conversational AI is the latest advancement in natural language processing (NLP) technology, aided by new breakthroughs in machine learning from companies like Google and OpenAI. While researchers have tried to teach computers how to replicate human language for decades, those efforts have accelerated significantly in recent years. For example, a modern chatbot like ChatGPT can understand and talk about a variety of topics in different language styles.
At the heart of modern-day conversational AI lies state-of-the-art large language models. These are machine learning models that have been trained on large datasets, including text from books, Wikipedia, and even social media platforms. As the training goes on, the model identifies patterns in the text and forms relationships between words and sentences. This doesn’t just let the model understand conversations, but also generate entirely new text that it has never encountered before.
Conversational AI refers to advanced models that can understand and respond to nuanced human dialogue.
Conversational AI isn’t just limited to the written word either. We now have convincing voice engines that can read AI-generated text with near-perfect intonation, tone, and emotion. I recently wrote about ChatGPT’s voice chat mode, for example, and its ability to sound human by adding pauses and sounds of hesitation.
I’ve mentioned ChatGPT a few times so far, mostly because it’s the most recognizable conversational AI around today. ChatGPT uses a slightly different version of GPT-3.5 or GPT-4 that’s specifically fine-tuned to mimic human dialogue. In other words, ChatGPT itself is an example of conversational AI but its underlying language model isn’t necessarily deserving of the same title.
How does conversational AI work?
In 2017, a group of Google researchers published a paper titled “Attention Is All You Need”. In it, they proposed a novel neural network architecture called the Transformer, which allows natural language models to selectively focus on key parts of a sentence to understand context, sentiment, and the greater meaning of a text sample. Earlier architectures couldn’t link words and sentences in the same way, which is why they couldn’t understand or replicate human speech very well.
Today, the Transformer architecture forms the backbone of most large language models (LLMs). These models are trained on gigabytes of text, scraped from all corners of the internet to understand how humans form sentences.
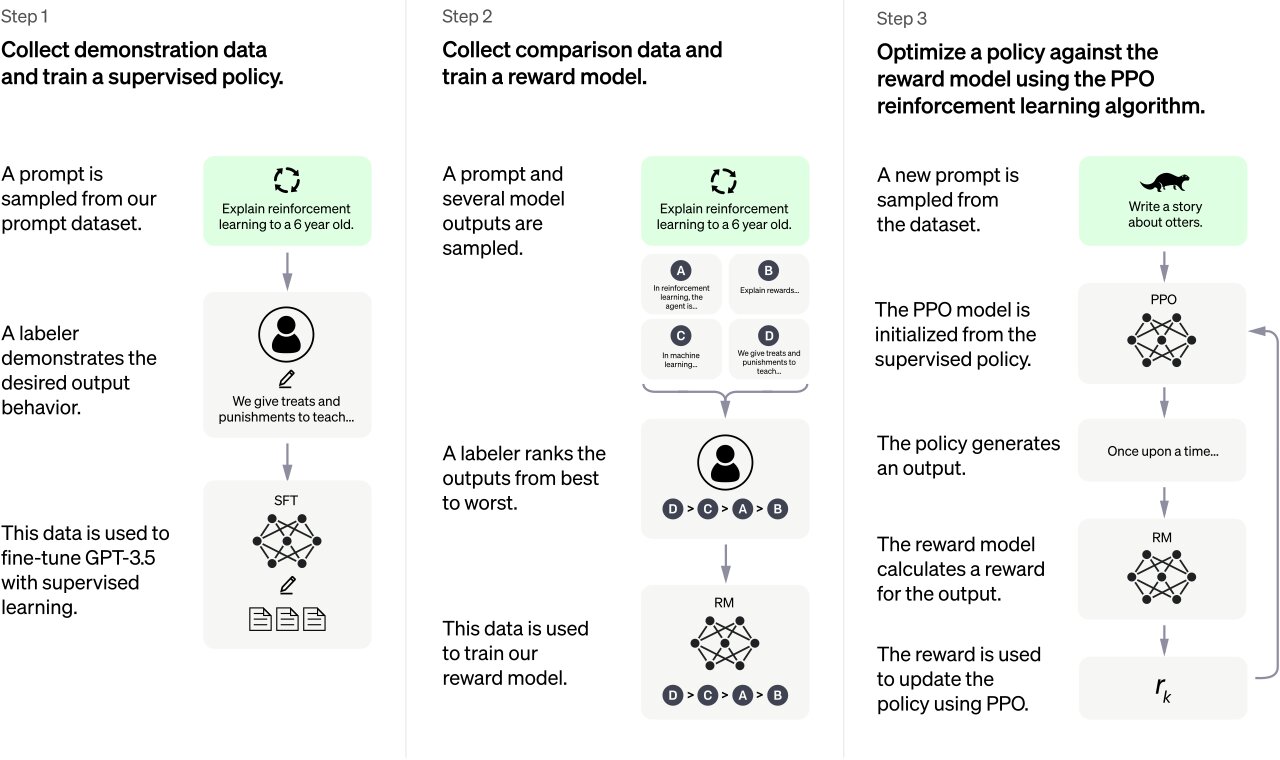
ChatGPT creator OpenAI took the Transformer architecture one step further and employed a technique known as Reinforcement Learning with Human Feedback (pictured above). It essentially involved hiring humans to rate thousands of text samples, which eventually trained the AI to sound more natural. You can also participate in this rating process if you upvote or downvote responses while using ChatGPT.
Most conversational AI relied on humans to rate their responses at some point during their training process.
Google has used a similar human-based approach to training its conversational AI products like Bard. In its report on the PaLM 2 language model, the company stated, “Hourly rates for workers depend on how fast judgements were completed. Most raters will have earned between $0.90/hour (at one comment per minute) to $5.40/hour (at 6 comments per minute), which aligns with typical hourly pay in the geographic regions where most raters are located.” I encourage reading the full report if you’d like to understand how modern AI systems are trained and aligned to sound more human.
Conversational AI vs generative AI vs chatbots: What’s the difference?
Besides conversational AI, you may have also come across terms like chatbots and generative AI. There’s no clearly defined boundaries between these terms and you may even notice a good degree of overlap.
Let’s start with chatbots, which is the oldest term of the three. Early chatbots worked on a very rudimentary rule-based mechanism. You’d essentially type in a few pre-programmed responses and try to capture all possible commands. However, traditional chatbots almost always fail when presented with a unique question or unseen command. You may have experienced this frustration when interacting with a Google Assistant or Alexa-powered smart speaker.
Moving on to conversational AI, it’s a term used to describe state-of-the-art chatbots that can respond to just about any human dialogue. It doesn’t need pre-programming to simulate conversation as it has learned to understand context and respond in a realistic manner.
Generative AI forms the backbone of many conversational AI platforms, but it's also capable of much more.
Finally, we have generative AI. It’s the technology underpinning many modern conversational AI services. The term describes AI that can generate different kinds of content, ranging from text to images and even voices. Midjourney and Bing Image Creator are examples of generative AI as they can create entire images that have never existed before.
Put simply, conversational AI like ChatGPT may fall under the category of both, chatbots and generative AI. However, more rudimentary chatbots like Alexa do not have any generative features built-in and may not deserve the conversational AI title either.
Benefits and drawbacks of conversational AI
Like any emerging technology, conversational AI has its pros and cons. Here are some of them:
- Efficiency: Imagine offloading tasks like document or meeting summarization to a chatbot. Using conversational and generative AI, we could all free up time to work on tasks that truly matter.
- On-demand help: Conversational AI can assist with mundane tasks like writing boilerplate code or even real-world jobs — imagine asking for help with changing your car’s tyre when you’re stranded in the middle of nowhere. A conversational AI could walk you through the steps in plain English and answer any unexpected questions you may have along the way.
- Biases: Depending on the dataset, conversational AI can amplify racial or gender biases by parroting stereotypes or supporting certain ideologies. These are often unintended, but are inevitable in any AI system trained on a variety of topics.
- Misinformation: Within the first few weeks of their release, ChatGPT and Bing Chat responded with made-up information. This phenomenon is known as hallucinating and it’s an ongoing challenge in the generative AI space.
Examples of conversational AI

We’ve witnessed an explosion in conversational AI of late, which means we now have many services to choose from. Some specialize in problem-solving and fact-finding like a human would, while others limit themselves to serving as a creative companion. With that diversity in mind, here are a few examples of conversational AI services you can use today:
- ChatGPT: OpenAI arguably kick-started the hype around conversational AI with ChatGPT when it threw open access to the chatbot in late 2022. Most of the services below only opened up to the public in response to ChatGPT.
- Google Bard: Google moved swiftly in the wake of ChatGPT’s release and in early 2023, the company unveiled Bard to the world. It uses the search giant’s own Gemini language model instead of GPT, which has been similarly fine-tuned for dialogue. I’ve personally found that Bard performs well in creative tasks but tends to make factual errors when asked about complex topics.
- Character.AI: Unlike the other conversational AI services on this list, Character.AI allows you to simulate chats with famous personalities. This means you can chat with impersonations of real-world celebrities like Elon Musk or bring comic book characters to life.
- Claude: Built by ex-OpenAI researchers, Claude is an AI assistant that prioritizes safe and honest responses above everything else. It was trained on a smaller, vetted dataset to reduce the chances of bias and unsafe responses.
- Microsoft Copilot: Built on the same foundation as ChatGPT, you’ll find Copilot baked into a variety of Microsoft products like Windows 11 and Bing. It’s also capable of searching the internet for new information and generating or analyzing images.
We will no doubt see even more conversational AI services in the coming months and years. Google’s Assistant with Bard, for example, marries the traditional chatbot experience with generative AI smarts. And with the current pace of innovation, the technology may soon become an integral part of our everyday lives.
FAQs
Yes, ChatGPT is an example of conversational AI — it can understand nuances in complex sentences and respond in a human-like manner.
Conversational AI is important to many because it’s like having a personal assistant that’s tailored to your specific needs and tasks. You can equate the cultural impact of conversational AI to early calculators, which automated simple calculations and freed us up to handle other tasks.
Conversational AI services are typically trained on very large datasets, which may include thousands of books, entire websites like Wikipedia, and even social media feeds like Twitter and Reddit. This allows the AI to become knowledgeable about different subjects and respond in varied tones.