Affiliate links on Android Authority may earn us a commission. Learn more.
What is an SSL certificate, why is it important and how to get one?

Have you ever noticed the padlock symbol in your web browser’s address bar? Most websites, including the one you’re reading this article on, use SSL certificates to establish a secure connection. The padlock icon offers a visual indication that the website has a valid SSL certificate installed. It also signals that any information you enter on the website is fully encrypted in transit. In other words, nobody can eavesdrop on your connection and steal sensitive data like your password or credit card details.
But what exactly are SSL certificates, how do they work, and can anyone get one? Here’s everything you need to know.
What is an SSL certificate and how does it work?
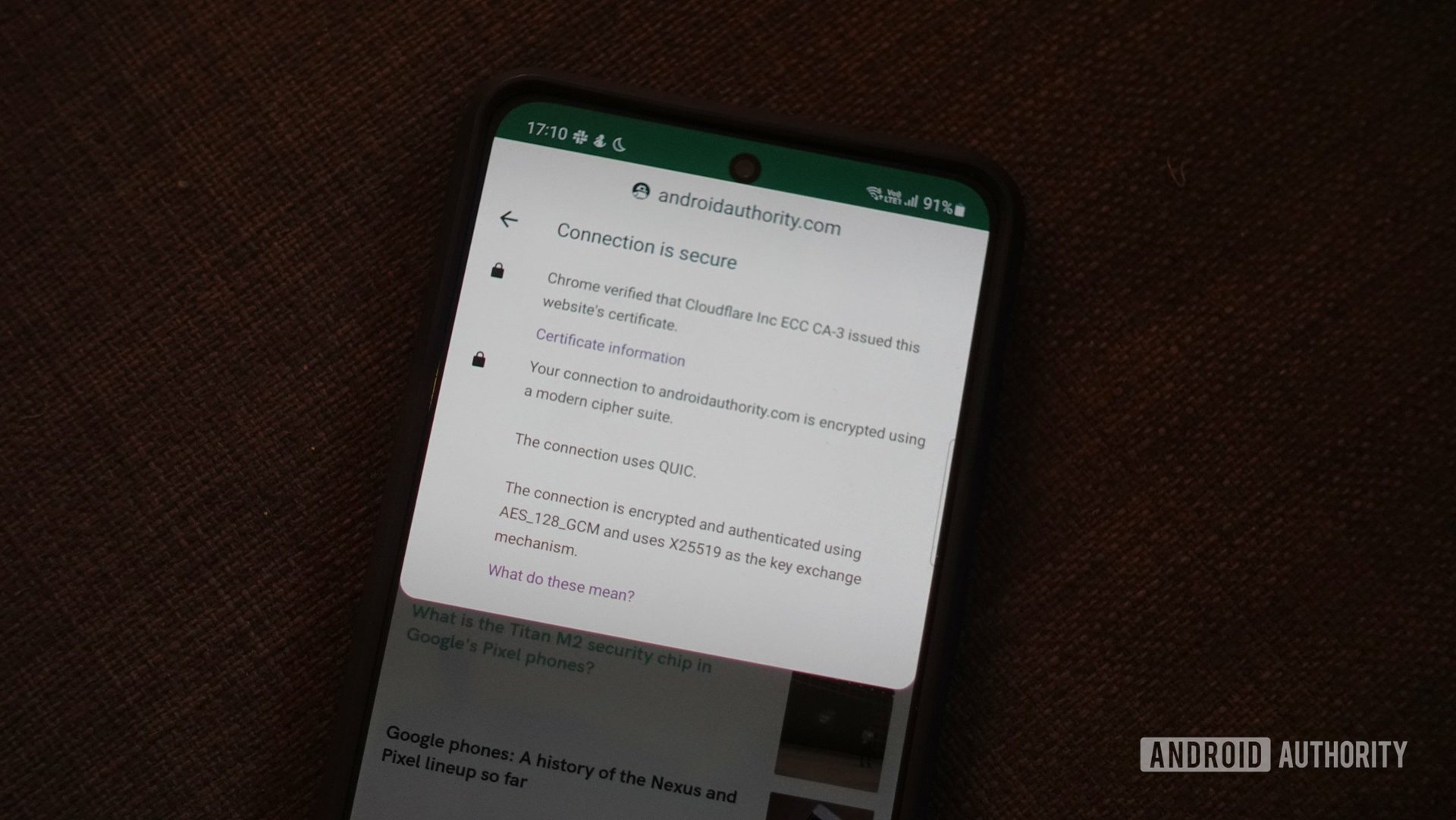
An SSL certificate is a digital certificate issued by a trusted authority used for HTTPS or secure connections on the Internet. A properly signed certificate provides a few key pieces of information that help your computer identify the identity of a website. It typically includes the name of the certificate owner, a unique serial number, an expiration date, and the digital signature of the issuing Certificate Authority (CA).
When you visit a website, your browser will automatically initiate a handshake process that checks for a valid SSL certificate. This process involves exchanging the SSL certificate and cryptographic keys, both of which cannot be spoofed.
SSL certificates aren't just symbolic, they also help keep your passwords safe from prying eyes.
If the details shared by the web server correspond to a valid certificate issued by a trusted authority, your browser will display a padlock symbol in the address bar. It will then initiate a secure connection, ensuring that data sent back and forth is completely encrypted.
In a nutshell, the server and web browser use the pieces of information they know about each other to generate a cryptographic key at each end. And since nobody else has access to these details, they won’t have the key to decrypt your communications.
If your web browser claims that the website you’re trying to access is insecure, chances are that it’s because of an invalid or expired SSL certificate. This can happen if the website owner forgets to renew their certificate, but if it happens on every single website, you should also check your system date and time. However, it could also mean that the website isn’t trustworthy so double-check that you’ve entered the correct address. Without an encrypted connection, you shouldn’t enter any sensitive information like passwords as your browser will send it in unencrypted plain-text.
Do I need an SSL certificate?
If you’re a website owner, getting an SSL certificate should be your top priority. This is especially true if you collect personal information or even user input in general. SSL certificates help ensure that a hacker can’t intercept any data sent back and forth, so there’s also privacy at stake.
Most web browsers these days, including Google Chrome, warn users if they visit a non-HTTPS website, which will likely cause them to click away. Search engines like Google also rank websites with SSL enabled higher so you’re incentivized to install a certificate.
If you don’t run a web or mail server, however, you don’t need an SSL certificate. As long as you have a modern, up-to-date web browser, it’s the website’s responsibility to ensure a secure connection.
How to get an SSL certificate

If you do need an SSL certificate, don’t worry – getting one doesn’t take too much effort. A certificate is essentially a file that lives on your web server, all you have to do is place it in the right location and ensure that your host provides it to visitors. While you can self-sign your own certificates, web browsers won’t accept those as they lack the signature of a trusted authority.
You can self-sign your own digital certificate, but no web browser will accept it for secure connections.
The easiest way to get a valid SSL certificate is via your domain provider’s website. GoDaddy, for example, will provide a single-domain SSL certificate at a fee of $299.99 every three years. DigiCert, meanwhile, offers certificates starting at $268 per year. And if you want a certificate for cheaper, other providers like NameCheap will have you covered for as little as $11 a year.
You can also get a valid SSL certificate for free via Let’s Encrypt, which works just fine for a personal website or even a small business. Let’s Encrypt is a non-profit Certificate Authority (CA) that aims to make internet security and encryption more widely accessible. The only downside is that you’ll have to renew and reinstall your digital certificate every three months instead of every year or longer. That said, you can automate this process with a small bit of code running on your web server.
Why are digital certificates so expensive?
If you’re wondering why the cost of a digital certificate varies so much, it’s because each one offers a different level of security and there are very few trusted authorities out there. Some CAs have humans manually review each domain before issuing a certificate. Naturally, this makes them inherently more trustworthy but also expensive. Premium SSL certificates may also display the name of the website owner in some web browsers (like Google Inc.), boosting the perceived legitimacy of the brand.
The price for a digital certificate can vary from $0 to hundreds of dollars, but for good reason.
For large businesses like banks where security matters above everything else, an SSL certificate is often a no-brainer. It also helps that many larger providers offer dedicated customer support and insurance in case something goes wrong.
Read more: What is a VPN, and why do you need one?