Affiliate links on Android Authority may earn us a commission. Learn more.
Forget antireflective films, future glass may come with antireflective surface
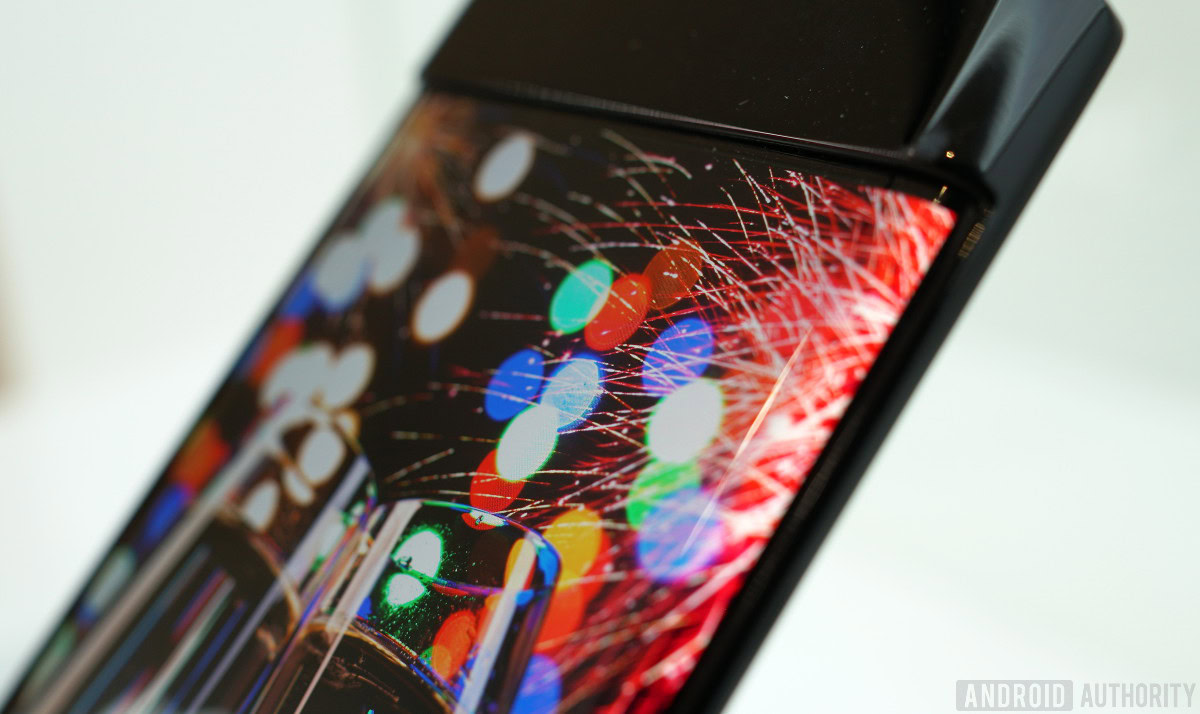

You may never again need to buy antireflective films for your phone thanks to these nanostructured glass panels.
Most electronic devices – including smartphones – come with glass panels which protect the displays underneath from damage or contamination. While durable, glass is highly reflective, which becomes an even larger problem when used with display technologies such as OLED that are not as bright as traditional LCD panels. One possible solution is to buy antireflective films, but not everyone likes those aesthetically-speaking, and more importantly, they eventually rip or peel. So, are smartphones fated to suffer from reflection issues forever?
A team of researchers headed by Andreas Liapis is likely to answer that in the negative: they have developed a special surface for glass, comprised of highly transmissive nanoscale cones, which substantially improves the readability of the screen even under direct sunlight. As Display Daily points out, “At normal incidence, glass in air has a 4% reflective loss at each surface, the loss growing larger with increasing angle of incidence… This loss is not a trivial problem in that this reflection manifests as glare.”
Liapis’ team is addressing that issue by creating a nanostructured surface on which copolymer materials are assembled. The subsequent etching of the glass surface and the formation of the nanostructures take place on this template, effectively transforming the surface of the glass into a forest of “highly transmissive nonoscale cones.” These cones, with their sharp tips, are modeled after the optical properties of antireflective films, according to the researchers.
The team has found that the average transmission of visible light remained higher than 90% even at 70 degrees from the surface normal.
In multiple experiments, the team has found that the average transmission of visible light remained higher than 90% even at 70 degrees from the surface normal. While this isn’t the first study to report the antireflective nature of nanoscale structures, Liapis’ report would be one of the first attempts by researchers to develop a commercially viable means to produce antireflective nanostructured surfaces.
For more information, you can read the full report here, titled “Self-assembled Nanotextures Impart Broadband Transparency to Glass Windows and Solar Cell Encapsulants.”