Affiliate links on Android Authority may earn us a commission. Learn more.
Snapdragon 800 vs Snapdragon 801

Hardware wise, the launches of the Samsung Galaxy S5 and Sony Xperia Z2 have been a little bit difficult to judge. First there was some confusion over which Snapdragon chip would actually ship in the Galaxy S5, then the octo-core version appeared, and now we’re left trying to tell exactly how much of an improvement Samsung’s and Sony’s handsets actually offer over the previous generation.
To make this situation even more confusing, Qualcomm releases lots of different SoC variations within each generation, and the Snapdragon 800 generation is one of the busiest. There’s the 8074, found in the Xperia Z Ultra WiFi edition, the 8274 for the HSPA+ Z Ultra, the 8974-AB, and the most popular 8974 which powers a lot of last generations’ handsets, like the Nexus 5. And that’s not even all of them. As you can see, attempting to compare processors can be a tricky business, so here’s a breakdown which hopefully clears up any confusion.
Which witch is which?
Firstly, we need to know exactly which handsets are using which processors, and this again is a point of potential confusion. The Samsung Galaxy S5 is confirmed to be using the Snapdragon 801 MSM8974AC chip, which is Qualcomm’s high end (bar the Snapdragon 805, but no handsets are confirmed to be using it yet). The Xperia Z2 is also listed as using a Snapdragon 801 SoC, but the model number is actually MSM8974AB, which is the same processor model as the Snapdragon 800 powered Samsung Galaxy Round. What gives?
It seems that somewhere in the lead up to the Xperia Z2’s launch, Qualcomm decided, or perhaps was nudged, to create a new revision of the MSM8974AB and upgraded it to Snapdragon 801 status. Although I can’t find anything to suggest that any components have undergone any changes between the Snapdragon 800 and 801 versions.

Then there’s the older MSM8974 Snapdragon 800 chip to consider, which powers many current top of the line handsets, including the LG G2, Nexus 5, and Sony’s Xperia Z1. Is Sony’s Xperia Z2 any different from this chip, and how different are both of these to Samsung’s Galaxy S5? Let’s find out.
Specs time
The table below details the hardware differences between the three different Snapdragon 800/801 chips used in top-tier smartphones. I’ve also thrown in a comparison with the older Snapdragon 600 for good measure.
| APQ8064T (Snapdragon 600) | MSM8974 (Snapdragon 800) | MSM8974AB (Snapdragon 800/801) | MSM8974AC (Snapdragon 801) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
CPU Cores | APQ8064T (Snapdragon 600) Krait 300 | MSM8974 (Snapdragon 800) Krait 400 | MSM8974AB (Snapdragon 800/801) Krait 400 | MSM8974AC (Snapdragon 801) Krait 400 |
Core Count | APQ8064T (Snapdragon 600) 4 | MSM8974 (Snapdragon 800) 4 | MSM8974AB (Snapdragon 800/801) 4 | MSM8974AC (Snapdragon 801) 4 |
CPU Frequency | APQ8064T (Snapdragon 600) 1900 MHz | MSM8974 (Snapdragon 800) 2260 Mhz | MSM8974AB (Snapdragon 800/801) 2260 Mhz | MSM8974AC (Snapdragon 801) 2450 Mhz |
GPU | APQ8064T (Snapdragon 600) Adreno 320 | MSM8974 (Snapdragon 800) Adreno 330 | MSM8974AB (Snapdragon 800/801) Adreno 330 | MSM8974AC (Snapdragon 801) Adreno 330 |
GPU Frequency | APQ8064T (Snapdragon 600) 450 MHz | MSM8974 (Snapdragon 800) 450 Mhz | MSM8974AB (Snapdragon 800/801) 550 MHz | MSM8974AC (Snapdragon 801) 578 MHz |
Process | APQ8064T (Snapdragon 600) 28nm LP | MSM8974 (Snapdragon 800) 28nm HPm | MSM8974AB (Snapdragon 800/801) 28nm HPm | MSM8974AC (Snapdragon 801) 28nm HPm |
Memory Type | APQ8064T (Snapdragon 600) 2 x LPDDR3 | MSM8974 (Snapdragon 800) 2 x LPDDR3 | MSM8974AB (Snapdragon 800/801) 2 x LPDDR3 | MSM8974AC (Snapdragon 801) 2 x LPDDR3 |
Memory Speed | APQ8064T (Snapdragon 600) 600 Mhz | MSM8974 (Snapdragon 800) 800 Mhz | MSM8974AB (Snapdragon 800/801) 933 Mhz | MSM8974AC (Snapdragon 801) 933 Mhz |
ISP Frequency | APQ8064T (Snapdragon 600) n/a | MSM8974 (Snapdragon 800) 320 MHz | MSM8974AB (Snapdragon 800/801) 465 Mhz | MSM8974AC (Snapdragon 801) 465 Mhz |
Camera Support | APQ8064T (Snapdragon 600) 21 MP | MSM8974 (Snapdragon 800) 55MP | MSM8974AB (Snapdragon 800/801) 55MP | MSM8974AC (Snapdragon 801) 55MP |
Video Encode | APQ8064T (Snapdragon 600) 1080p | MSM8974 (Snapdragon 800) 2160p | MSM8974AB (Snapdragon 800/801) 2160p | MSM8974AC (Snapdragon 801) 2160p |
Example Smartphones | APQ8064T (Snapdragon 600) HTC One, Samsung Galaxy S4 (I9505) | MSM8974 (Snapdragon 800) LG G2, LG G Flex, LG Nexus 5, Samsung Galaxy S4 LTE+, Sony Xperia Z1 | MSM8974AB (Snapdragon 800/801) Samsung Galaxy Round, Sony Xperia Z2 | MSM8974AC (Snapdragon 801) Samsung Galaxy S5 |
As you should be able to see, there’s a fair bit of overlap between the MSM8974, MSM8974AB, and MSM8974AC. The Snapdragon 800 and 801 SoCs all share the same four Krait 400 CPU core configurations and the same Adreno 330 graphics chip, compared with the older Snapdragon 600 which is built on the older Krait 300 architecture and slower Adreno 320 GPU. The clock speeds are the only changes between the Snap 80X chips, with the 8974AC 801 bumping the peak frequency up to 2.5 GHz, an 8 percent increase.
GPU wise the biggest jump appears between the older Snapdragon 800 8974 and the Xperia Z2s 8974AB, which offers a 22 percent increase in speeds. The gap with the Galaxy S5s 8974AC chip is even larger, at 28 percent, but between the Xperia Z2 and the GS5 there’s just a 5 percent difference in GPU frequency.
Memory wise, all the SoCs are using the same LPDDR3 memory base but with improved memory speeds between the 600, 800, and 801 chips, although the effect of this clock increase is likely to be negligible for the user.
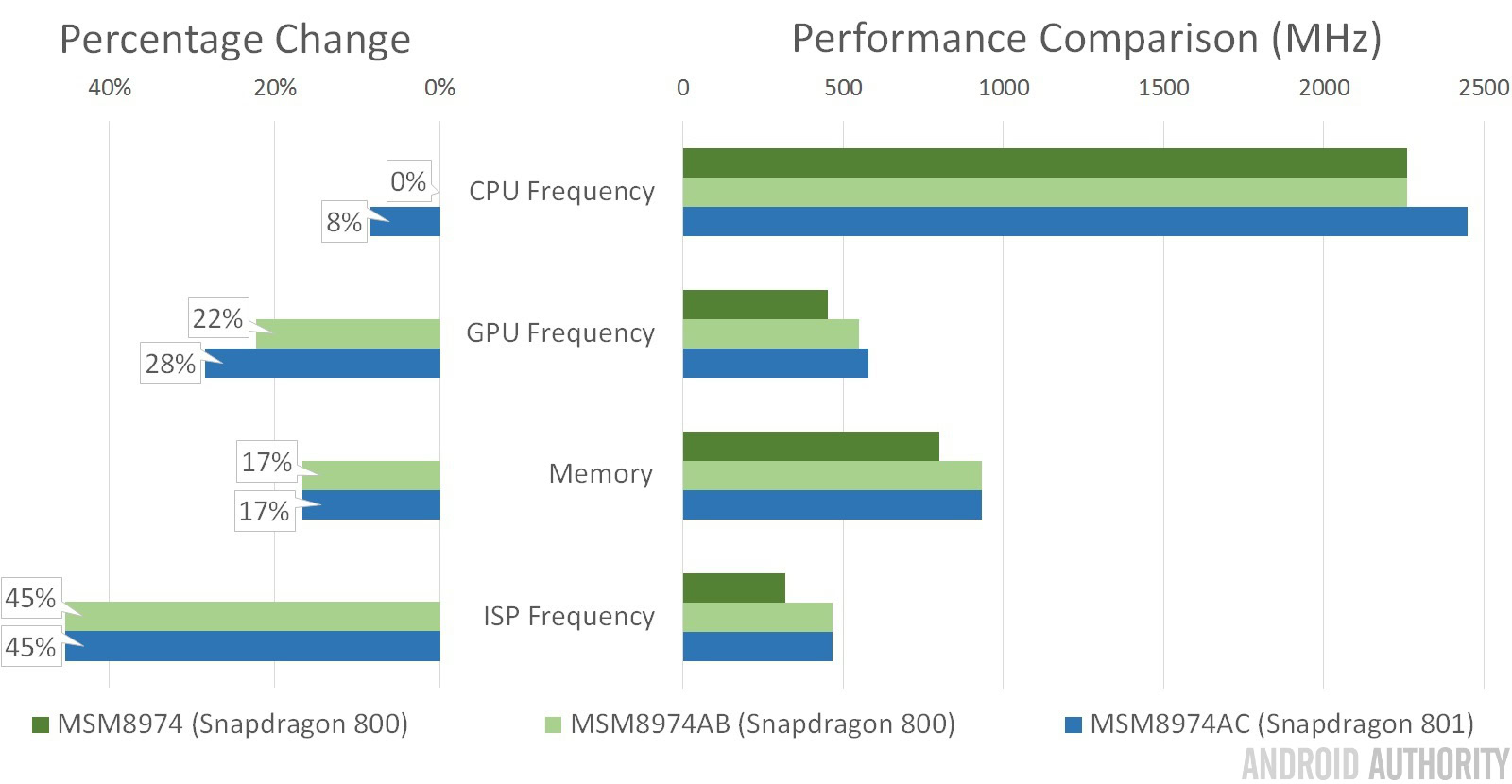
All of the Snapdragon 80X chips have an additional individual ISP (image signal processor) chip for handling image and video processing, and here’s where one of the biggest improvements appears between the older Snapdragon 800 SoCs and the new 801 versions. The ISP clock frequency has been increased by 45% with the 8974AB and AC, resulting in a 465MHz clock speed, and throughput has been bumped up to 1GPixelsl/s class compared to 640MPixels/s for Snapdragon 800 (320MHz).
Each of the SoC revisions also have a few defining features, the 8974AC makes the move to eMMC 5.0, which enables support for a faster 400MB/s flash memory speeds, making the chip compatible with quicker flash storage options, such as the iNAND Extreme from SanDisk. Both the 8974AB and AC also squeezes in support for DS-DA (dual-sim, dual-active) to the modem, whilst retaining Category 4 LTE compatibility from the original Snapdragon 800 chip.
What this means for smartphone performance
Finally, we can make a decision about the real differences between Qualcomm’s various SoCs. The Xperia Z2’s SoC sits in somewhat of a middle ground between the higher CPU clocked Galaxy S5, but with a boosted GPU compared with the older Snapdragon 800 handsets.

The Galaxy S5’s chip (8974AC) is technically the fastest, with its 2.5 GHz CPU and 578 MHz GPU clock speeds, followed very closely by the Xperia Z2 (8974AB). Compared with the old Snapdragon 600 there’s no contest, there are superior chips in every way. But compared with the Snapdragon 800 chip (8974) already on the market, the only real performance boost comes in terms of the GPU and IPS. The increased GPU clock speeds makes these new devices the clear choice for those in need of extra gaming performance and if you’re really into video recording, but in terms of general day-to-day performance you’re not going to notice a difference compared with slightly older flagship devices, like the LG G2. Future 8974AC powered devices, like the Galaxy S5, will also have exclusive access to faster flash memory and MicroSD cards, via eMMC 5.0.
The key point to note is that the Galaxy S5 and Xperia Z2’s SoCs have both received some modest performance boosts over the older Snapdragon 800 chip, but there are remain slight differences between the two of them worth noting, and worth scrutinizing. Of course, there’s a lot more to choosing a handset than just the processor, especially when there’s very little to choose between them. Battery life, display size, and storage options all form equally important parts of your day to experience. Flagship devices of today represent best of breed tech, and absolutely fly. No matter what you opt for, you’re going to have a remarkable experience.
Were you disappointed at the absence of Snapdragon 805 powered fla