Affiliate links on Android Authority may earn us a commission. Learn more.
What is NVIDIA DLSS? NVIDIA Deep Learning Super Sampling explained
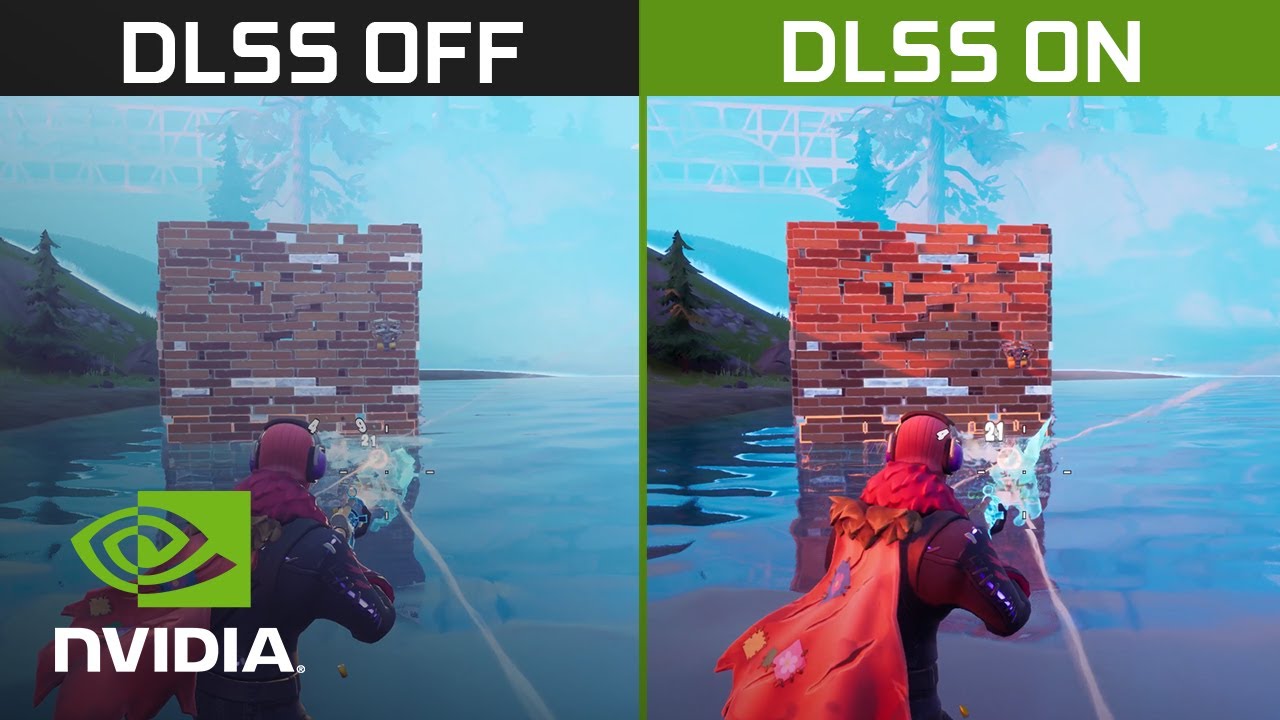

NVIDIA has some of the best GPU hardware out there, but that’s not the whole reason for its success. Over the years, NVIDIA has consistently worked to make its software implementations back up its powerful GPUs, and that shows in the product offerings it has today. One of these implementations is NVIDIA Deep Learning Super Sampling, better known as NVIDIA DLSS.
NVIDIA introduced DLSS as a feature to go along with its RTX lineup of GPUs. Starting with Series 20 RTX GPUs back in September 2018, NVIDIA DLSS aimed to offset some of the extra effort needed to output ray-traced graphics. It is a nice visual quality and FPS gain to give your RTX GPUs a boost in performance. Let’s take a deeper look at it.
Also read: What is G-Sync? NVIDIA’s display synchronization technology explained
What is NVIDIA DLSS and how does it work?
To put it simply, NVIDIA DLSS is an AI-based supersampling technology that can make your games look better in terms of quality as well as frame rates. DLSS stands for Deep Learning Super Sampling. It’s NVIDIA’s tale on supersampling, which is an anti-aliasing technology that takes color samples of the pixels in an image at different instances. Supersampling renders the image at a much higher resolution and uses the data from those images to add detail to the native resolution image. This means you can get a much higher quality image output, with the jagged edges and other artifacts cleaned up.
NVIDIA DLSS uses deep learning to improve this supersampling drastically. A neural network using NVIDIA’s AI is trained with high-resolution images. This machine learning teaches the network how to efficiently add detail to the native resolution images. The big advantage here is that all this training isn’t done locally, on your computer, but rather on NVIDIA’s supercomputer. The overall work your GPU has to do is thus drastically reduced.
DLSS is thus a huge exercise that involves training NVIDIA’s neural network. NVIDIA’s RTX lineup-exclusive Tensor cores then do the basic processing. The end result is a quality boost, as well as a significant FPS boost, hitting improvements of over 50% in frame rates, in some cases. The performance gain has gotten a boost with the arrival of DLSS 2.0.
Also read: NVIDIA GPU guide: All NVIDIA GPUs explained, and the best NVIDIA GPU for you
DLSS 2.0 — How it changed the game
DLSS 2.0 came out in March 2020, promising great improvements over the first version. NVIDIA DLSS had a bit of an adaptation curve since developers and NVIDIA needed to work together to train the neural network for every single game. With DLSS 2.0, there is a universal neural network. This network is also backed by an improved algorithm, which gathers data from multiple frames over time, generates a high-quality output frame, and then feeds the frame to the network again to use the data to improve the next frame. This data includes motion vectors that tell the AI the direction in which the objects are moving, and temporal feedback to help out with the timing.
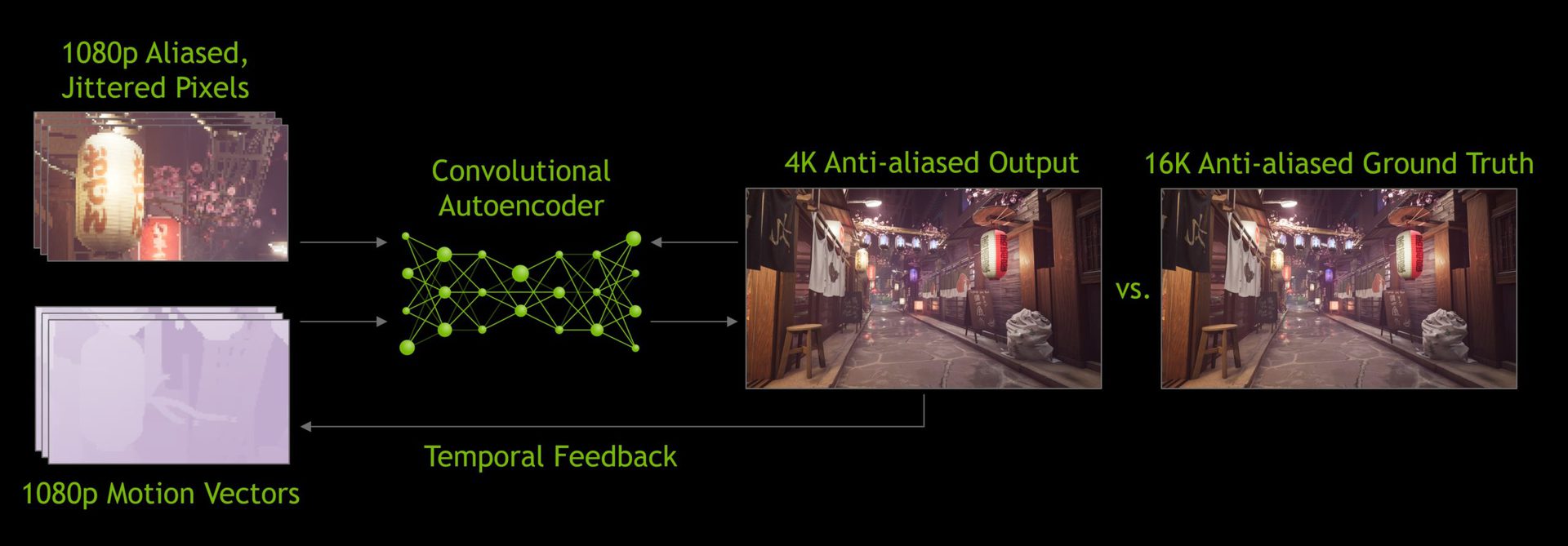
NVIDIA gave DLSS a do-over, using this new approach. NVIDIA claims to deliver better image quality and higher frame rates than native resolution. DLSS 2.0 also doesn’t have any resolution restrictions so you can play at any resolution you choose.
Coming to the quality presets, DLSS 2.0 has three — Performance, Quality, and Balanced. The Performance mode upscales the image to 4X for better frame rates. The Quality mode focuses on the visual quality, with only 2X upscaling. This means a lower FPS. The Balanced mode operates between the two, giving you a solid middle ground between frame rates and quality.
NVIDIA has followed this release with DLSS 2.1. It brings support for the latest gen RTX 30 GPUs. The new features added include a new Ultra Performance mode with 8K gaming and 9X scaling for the RTX 3090. Also present is support for VR titles and dynamic resolution.
Also read: AMD vs NVIDIA – what’s the best add-in GPU for you?
NVIDIA DLSS vs AMD FidelityFX Super Resolution
AMD FidelityFX Super Resolution is AMD’s answer to NVIDIA DLSS. The two seem like equivalents on paper, but AMD FSR is actually quite simpler. It does not use any sort of learning or AI. Instead, it more like with your typical upscaling technology, with some extra effort.
AMD FidelityFX Super Resolution will take a low-res image and put it through two upscaling networks, linear and non-linear. It picks out different features of the images through each of the two pathways. It then puts all the data together to create a pixel grid and expands it to make a higher resolution image, which is cleaned up and outputted. This is done on the go, locally.
The end result is that the image output is far from being on the same level as DLSS. At least that’s what we can tell from the demo that we have seen since FSR isn’t out in the market yet. Given the fact that AMD FSR is using traditional upscaling and not much else, it’s likely that the image quality will not match up.
There’s a significant advantage that AMD FSR has though, and that’s compatibility. It supports most recent AMD GPUs, as well as NVIDIA GPUs including GTX 10-series, and all RTX GPUs. There’s also support coming for Xbox Series X and S. On the other hand, NVIDIA DLSS is limited to NVIDIA RTX GPUs.
NVIDIA DLSS also required per-game training up until the company released 2.0. On the other hand, AMD FSR doesn’t need per-game training, to begin with. This means that adoption should be relatively easier. Even then, AMD will need to make a machine-learning-based supersampling equivalent to DLSS if it really wants to compete with NVIDIA.
Also read: What is AMD FidelityFX Super Resolution? AMD FSR explained
NVIDIA DLSS supported GPUs and games
NVIDIA DLSS only supports NVIDIA’s RTX lineup of GPUs. This includes the first generation RTX 20 series and the latest RTX 30 series of GPUs. As far as supported games go, here is a complete list of every game that supports NVIDIA DLSS.
| Game | Ray Tracing support |
|---|---|
AMID EVIL | |
Anthem | |
Aron's Adventure | |
Battlefield V | Yes |
Bright Memory | Yes |
Call of Duty: Black Ops Cold War | Yes |
Call of Duty: Modern Warfare | Yes |
Call of Duty: Warzone | |
Control | Yes |
CRSED F.O.A.D | |
Crysis Remastered | Yes |
Cyberpunk 2077 | Yes |
Death Stranding | |
Deliver Us The Moon | Yes |
Edge of Eternity | |
Enlisted | |
Everspace 2 | Yes |
F1 2020 | |
Final Fantasy XV | |
Fortnite | Yes |
Ghostrunner | Yes |
Into the Radius VR | |
Iron Conflict | |
Justice | Yes |
Marvel's Avengers | |
Mechwarrior 5: Mercenaries | Yes |
Metro Exodus PC Enhanced Edition | Yes |
Minecraft with RTX | Yes |
Monster Hunter World | |
Moonlight Blade | Yes |
Mortal Shell | Yes |
Mount & Blade II: Bannerlord | |
NARAKA: BLADEPOINT | |
Nine To Five | |
Nioh 2 The Complete Edition | |
No Man's Sky | |
Outriders | |
Pumpkin Jack | Yes |
Qu Gian Qi Tan Online | |
Ready or Not | |
Redout: Space Assault | |
Scavengers | |
Shadow of the Tomb Raider | Yes |
Supraland | |
System Shock Demo | |
The Fabled Woods | Yes |
The Medium | Yes |
War Thunder | |
Watch Dogs: Legion | Yes |
Wolfenstein: Youngblood | Yes |
Wrench | Yes |
Xuan-Yuan Sword VII | Yes |
We expect DLSS to bring even bigger improvements with future versions. The DLSS machine learning has already shown great promise since its launch, and it gives us hope for the future of the implementation. NVIDIA has an edge with hardware, and DLSS is helping it maintain that edge. AMD could and should make a version of FSR that leverages machine learning at least on Radeon hardware, to give better performance, if it truly wants to match DLSS. Either way, this competition will only mean good things for the consumer/
Stay tuned for more on NVIDIA DLSS, PC graphics, and other relevant PC tech. In the meantime, check out these articles.