Affiliate links on Android Authority may earn us a commission. Learn more.
Intel's next-gen processor works similarly to Arm's big.Little configuration

- Intel has unveiled its 12th generation CPU architecture, to be available this fall.
- Called Alder Lake, it’s a hybrid architecture, bringing performance and efficiency cores on one chip.
- Intel also revealed Thread Director, a hardware solution for splitting the workload between cores, which will work best on Windows 11.
Intel has just unveiled its latest CPU architecture, Alder Lake. With this 12th generation iteration, the CPU giant is bringing a hybrid system-on-a-chip design, combining Efficiency Cores and Performance Cores on a single chip. With this upgrade, Intel is promising the best of both worlds — high performance with the Performance Cores, and power efficiency with the Efficiency Cores.
We have seen a lot of this model with the ARM big.Little architecture, and more recently in Apple’s M1 SoC, but Intel is now bringing it to x86 CPUs. While these architectures focus on efficiency first, since they’re designed for mobile devices, Intel notes that Alder Lake will focus on performance first.
Alder Lake will still use a 10nm process, now called Intel 7.
Intel Alder Lake: Performance and Efficiency cores, and Thread Director to rule them all

Intel compared its new Efficiency Cores with the older 14nm Skylake cores. Intel promises a 40% performance jump in single-thread tasks, while using the same amount of power, and 80% on multi-thread while using less power.
Then there are the Performance Cores, which Intel showed off in comparison to the 11th gen Cypress Core architecture. Intel is promising an average improvement of 19% over the last generation.
Juggling these two different types of cores will be Intel’s new hardware-based solution — Thread Director. The Thread Director will analyze a horde of different data to help the OS decide whether to delegate it to a Performance Core or an Efficiency Core. Intel says this technology will work best with Windows 11.
Also read: 5 big changes we can expect in Windows 11
On the core/thread count front, Intel says Alder Lake can go up to 16 cores, with 8 Performance and 8 Efficiency Cores. Each Performance Core will get up to two threads. On the other hand, each Efficiency Core will get only one thread, capping the maximum number of threads at 24.
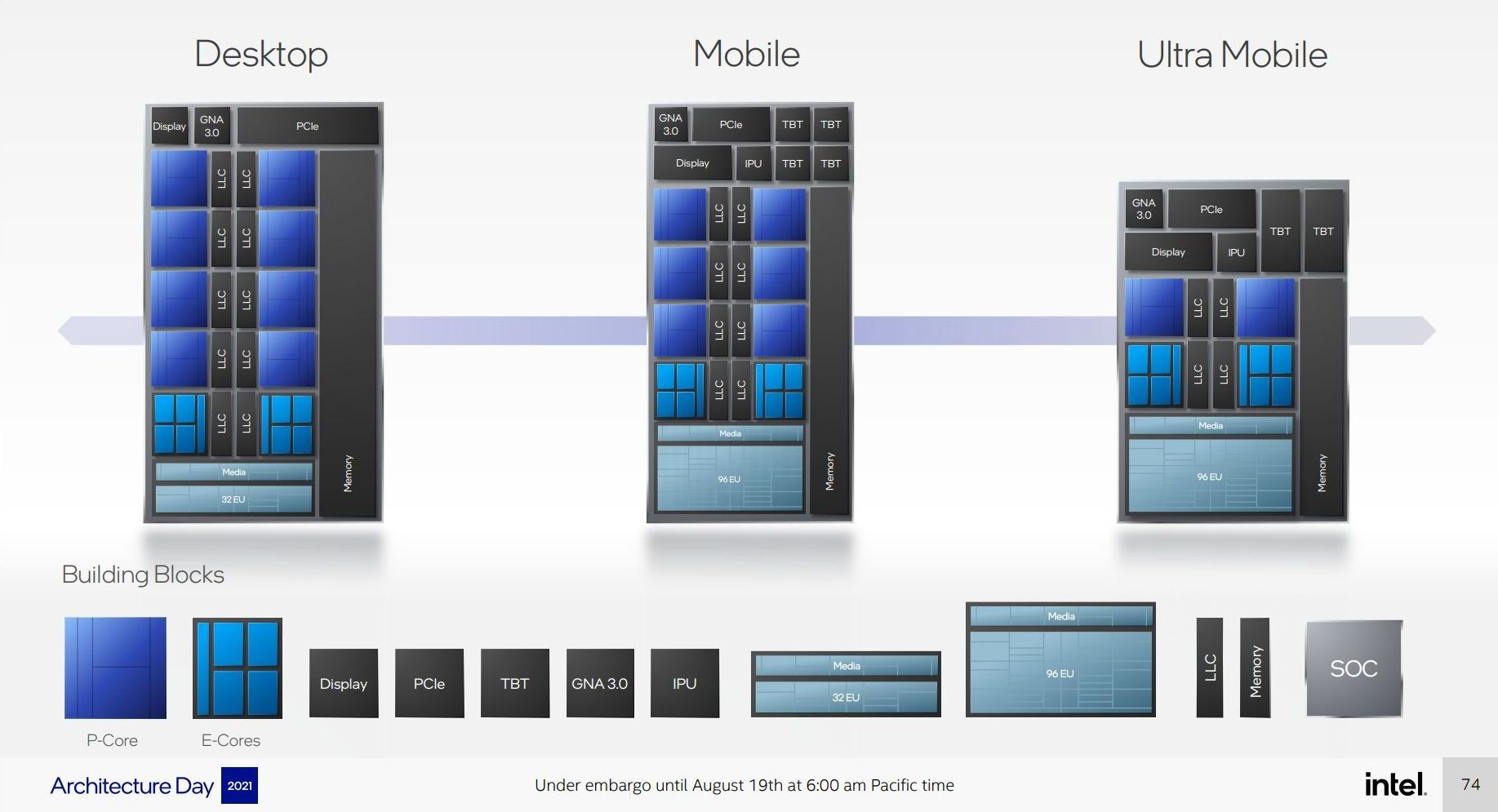
The eight Efficiency Cores will be a standard across desktop and mobile. The desktop versions will get the full-fat 8 Performance Core design. The mobile versions will get 6 or 2, depending upon the power requirements. The TDP will range from 9W for the “Ultra mobile” designs, and 125W for the maxed-out desktop version.
We’re also getting a unified memory controller that will be present on all of these chips. It will support DDR5 at 4800 MT/s, DDR4-3200, LPDDR5-5200, and LPDDR4X-4266. The desktop version will also get 20 lanes of PCIe, with up to 16 of these being PCIe 5.0.
Alder Lake will enter the market this fall. Intel will be revealing more information about Alder Lake in the coming months, including an exact launch date.